This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $980 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1420 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2130 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3104 CAS #: 25913-34-2 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Tinoridine HCl (also known as Y-3642 HCl), the hydrochloride of tinoridine (Y-3642), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that also has potent radical scavenger and antiperoxidative activity.
References: O Shimada, et al. Hydroxyl radical scavenging action of tinoridine. Agents Actions. 1986 Nov;19(3-4):208-14.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 352.88 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H21ClN2O2S |
| CAS No. | 25913-34-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
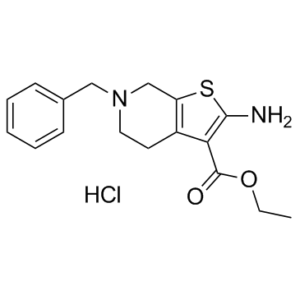
| SMILES Code | O=C(C1=C(N)SC2=C1CCN(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C2)OCC.Cl |
| Synonyms | Y3642; Y-3642 hydrochloride; Tinoridine hydrochloride; Tinoridine HCl; Y-3642; Y3642 HCl; Y3642 hydrochloride |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Tinoridine reduces a stable free radical, diphenyl-p-picrylhydrazyl, in the molar ratio of about 1:2, indicating its free radical scavenging ability. Tinoridine inhibits the lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes induced by xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of ADP and Fe2+, in which hydroxyl radical is formed. Tinoridine is demonstrated to be oxidized in the course of the lipid peroxidation by following the fluorescence derived from the oxidation product of tinoridine. It is also oxidized by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system in the presence of Fe2+, but its oxidation is slow in the absence of Fe2+ and almost completely inhibited by catalase. Tinoridine is also oxidized by H2O2-Fe2+ system producing OH (Fenton reaction), but it does not affect the reduction of cytochrome c caused by superoxide radical. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | CCl4 aministration produces a marked decrease in the concentrations of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and G6Pase, indicating that hepatic endoplasmic reticulum function is disrupted. Prior treatment of the animals with tinoridine (100 mg/kg) significantly reduces the CCl4-induced alterations in the enzyme activities, and a rapid recovery toward the normal values is observed. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.8338 mL | 14.1691 mL | 28.3382 mL | 56.6765 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5668 mL | 2.8338 mL | 5.6676 mL | 11.3353 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2834 mL | 1.4169 mL | 2.8338 mL | 5.6676 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1417 mL | 0.7085 mL | 1.4169 mL | 2.8338 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































