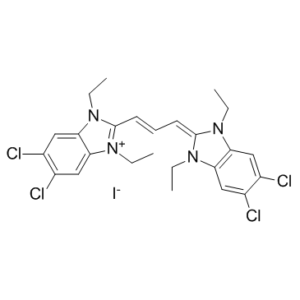
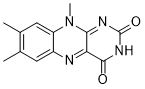
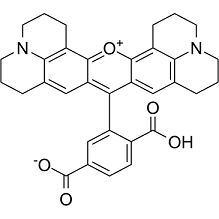
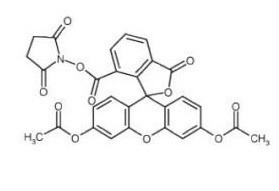
JC-1 can be used in a probe for measuring mitochondrial membrane potential by flow cytometry.
Lumiflavine (Lumilactoflavin), produced by the photolysis of vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), is a potent riboflavin uptake inhibitor used to study riboflavin uptake in intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) and other epithelial cells.
6-ROX (6-Carboxy-X-rhodamine) is a novel fluorescent oligonucleotide marker, acting as an acceptor molecule coupled to 5-FAM as the donor in FRET imaging.
CFSE [5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester; CFDA-SE; 5(6)-CFDA N-succinmidyl ester] is a novel, a cell-permeable and amine-reactive fluorescent dye which has been widely used to track cell division by covalently coupling, via its succinimidyl group, to intracellular molecules such as lysine residues and other amine sources. Specifically, it is used to monitor distinct generations of proliferating […]
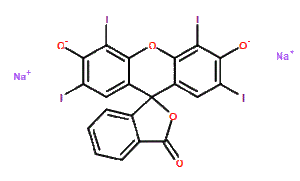
Erythrosine sodium (close form, CI-45430 CI45430; CI 45430) is a tetraiodofluorescein and a dye used as a fluorescent indicator in microscopy and for adsorption.
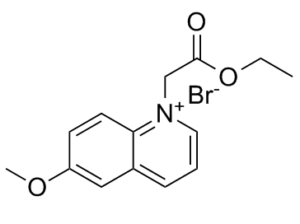
MQAE (N-[ethoxycarbonylmethyl]-6-methoxy-quinolinium bromide) is an analog of 6-methoxyquinolinium. It is a novel fluorescent indicator/dye for detection of intracellular Cl-. MQAE detects the ion when quenched via collision with chloride. It is more frequently used for chloride measurement as it is more sensitive and selective than 36Cl and microelectrode-based methods. MQAE is a useful fluorescence dye […]
Indocyanine Green (IC Green; Cardiogreen; Fox) is a non-toxic tricarbocyanine/fluorescent dye used diagnostically in liver function tests and to determine blood volume and cardiac output.
3,3′-Dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine perchlorate is a novel and potent green fluorescent lipophilic tracer.
Diphenylterazine (DTZ) is a novel bioluminescence agent that showed superior in vitro and in vivo sensitivity over commonly used bioluminescence reporters. As a Red-shifted bioluminescence reporter, it has the potential to be used for biological imaging.
X-GAL (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactoside), consisting of galactose linked to a substituted indole, is a histochemical substrate for β-galactosidase. This substrate yields a blue precipitate upon hydrolysis, making it suitable for use in immunoblotting or immunocytochemical assays., and thus is widely used a chromogenic β-galactosidase substrate. β-galactosidase cleaves X-gal and produce an insoluble blue compound, which is detectable. […]