This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 10mg | $50 | 3-6 Days |
| 50mg | $80 | 3-6 Days |
| 100mg | $120 | 3-6 Days |
| 250mg | $190 | 3-6 Days |
| 500mg | $290 | 3-6 Days |
| 1g | $470 | 3-6 Days |
Cat #: V0100 CAS #: 162558-52-3 Purity ≥ 98%
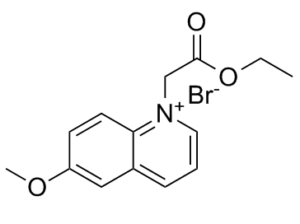
Description: MQAE (N-[ethoxycarbonylmethyl]-6-methoxy-quinolinium bromide) is an analog of 6-methoxyquinolinium. It is a novel fluorescent indicator/dye for detection of intracellular Cl-. MQAE detects the ion when quenched via collision with chloride. It is more frequently used for chloride measurement as it is more sensitive and selective than 36Cl and microelectrode-based methods. MQAE is a useful fluorescence dye for noninvasive measurements of the intracellular Cl-.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 326.19 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H16BrNO3 |
| CAS No. | 162558-52-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >30 mg/mL |
| Water: N/A | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| SMILES Code | COC1=CC2=CC=C[N+](CC(OCC)=O)=C2C=C1.[Br-] |
| Synonyms | N-[ethoxycarbonylmethyl]-6-methoxy-quinolinium bromide; MQAE; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: MQAE (N-[ethoxycarbonylmethyl]-6-methoxy-quinolinium bromide) is a novel fluorescent indicator/dye that is quenched via collision with chloride, and is more sensitive and selective than 36Cl and microelectrode-based methods for chloride measurement in cells. MQAE was used to measure intracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]i) in primary cultures of rat aortic smooth muscle cells (VSMC). The hydrolytic and fluorescent properties of the dye were characterized. The intracellular Stern-Volmer constant was calculated to be 25 M-1. Cl- efflux curves were characteristic of saturation-type kinetics, with an apparent Michaelis-Menten constant value of 11 +/- 4.8 (SD) mM, a maximum velocity of 0.038 +/- 0.021 mM/s, and a half time (t1/2) of 9.0 +/- 3.7 min. Kinase Assay: This protocol describes a technique for high-resolution chloride imaging of living cells using a quinoline-based chloride (Cl(-)) indicator dye, MQAE (N-[6-methoxyquinolyl] acetoethyl ester). Bath-applied to acute brain slices, MQAE provides high-quality labeling of neuronal cells and their processes. In living anesthetized mice, cortical cells are labeled using the multicell bolus loading procedure. In combination with two-photon microscopy, this procedure enables in vivo visualization of cell bodies of neurons and astrocytes as well as some astrocytic processes and allows one to monitor changes in the intracellular chloride concentration in dozens of individual cells. Cell Assay: The intracellular Stern-Volmer constant was calculated to be 25 M-1. Cl- efflux curves were characteristic of saturation-type kinetics, with an apparent Michaelis-Menten constant value of 11 +/- 4.8 (SD) mM, a maximum velocity of 0.038 +/- 0.021 mM/s, and a half time (t1/2) of 9.0 +/- 3.7 min. The average efflux rate in the first 10 min (0.023 +/- 0.004 mM/s) was reduced in the presence of either 130 microM 4,4'-diisothiocyanato-dihydrostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid (H2DIDS) (0.014 +/- 0.006, P = 0.02) or 40 microM furosemide (0.017 +/- 0.004, P = 0.04). Restoration of physiological extracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]o) after zero Cl- resulted in net Cl- influx with a t1/2 of 3.6 +/- 1.0 min. The initial Cl- influx rate was reduced after exposure to furosemide, from 0.069 +/- 0.006 to 0.046 +/- 0.008 mM/s, P < 0.002, and was reduced after exposure to H2DIDS from 0.102 +/- 0.013 to 0.033 +/- 0.003 mM/s, P < 0.001. Furosemide reduced the steady-state [Cl-]i from 31.6 +/- 3.2 to 26.1 +/- 2.4 mM, P < 0.01, whereas H2DIDS had little effect on [Cl-]i. Our results demonstrate that MQAE can be used to measure [Cl-]i in primary cultures of VSMC. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In living anesthetized mice, cortical cells are labeled using the multicell bolus loading procedure. In combination with two-photon microscopy, this procedure enables in vivo visualization of cell bodies of neurons and astrocytes as well as some astrocytic processes and allows one to monitor changes in the intracellular chloride concentration in dozens of individual cells. | |
| Animal model | Mice |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.0657 mL | 15.3285 mL | 30.6570 mL | 61.3140 mL |
| 5mM | 0.6131 mL | 3.0657 mL | 6.1314 mL | 12.2628 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3066 mL | 1.5328 mL | 3.0657 mL | 6.1314 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1533 mL | 0.7664 mL | 1.5328 mL | 3.0657 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































