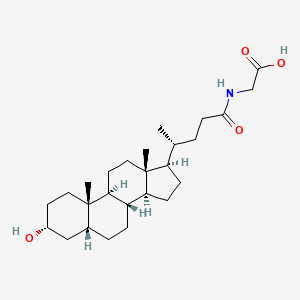
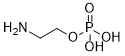Glycolithocholic acid (Lithocholic acid glycine conjugate; Lithocholylglycine) is a glycine conjugate (N-acylglycine) of lithocholic acid which is a secondary bile acid.
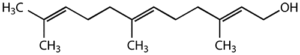
Farnesol (HSDB445; HSDB-445; HSDB 445) is an inducer of apoptosis in cell cultures.
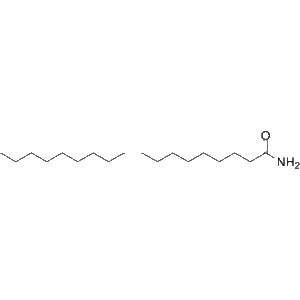
Oleamide is an endogenous fatty acid amide found in the nervous systems of mammalians, and can be detected in human plasma.
Phosphoethanolamine (also known as Phosphorylethanolamine, Monoaminoethyl phosphate; NSC 254167; O-Phosphoethanolamine) is used to construct glycerophospholipid and sphingomyelin or sphingophospholipid.
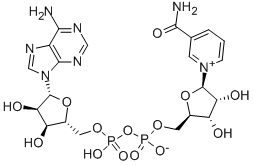
NAD+ is a naturally occurring coenzyme, oxidizing agent, and electron acceptor consisting of ribosylnicotinamide 5′-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5′-phosphate by a pyrophosphate linkage.
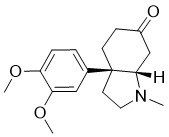
Mesembrine acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
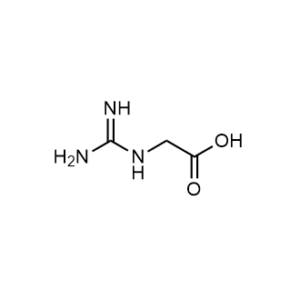
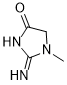
Glycocyamine is a novel and potent indicator agent and Reagent.
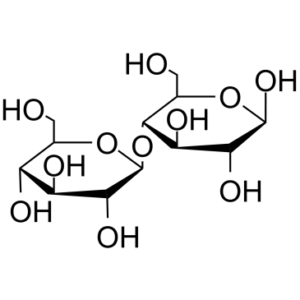
D-(+)-Cellobiose is an endogenous chemical/metabolite.
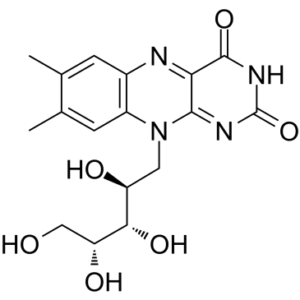
Riboflavin (also named as vitamin B2), a vitamin B class of compound, is a important nutrient that plays a key role in maintaining health in humans and other animals.
Creatinine (also known as NSC13123) is a degradation/break-down product of creatine phosphate in muscle, and is usually produced at a fairly constant rate by the body.