This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1020 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1480 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2220 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3819 CAS #: 124436-59-5 Purity ≥ 98%
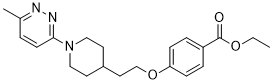
Description: Pirodavir (formerly known as R 77975) is the prototype of a novel class of broad-spectrum antipicornavirus compounds. It is a capsid-binding antipicornavirus agent with potent in vitro activity against both group A and group B rhinovirus serotypes. Although its predecessor, R 61837, a substituted phenyl-pyridazinamine, was effective in inhibiting 80% of 100 serotypes tested (EC80) at concentrations above 32 micrograms/ml, pirodavir inhibits the same percentage of viruses at 0.064 micrograms/ml. Pirodavir was one of the most promising capsid-binding compounds to show efficacy in human clinical trials for chemoprophylaxis of the common cold.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 369.46 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H27N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 124436-59-5 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mMr |
| Water: < 1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL | |
| Synonyms | Pirodavir; R 77975; R-77975; R77975; R77,975; R 77,975; R-77,975; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Pirodavir (formerly known as R 77975) is the prototype of a novel class of broad-spectrum antipicornavirus compounds. It is a capsid-binding antipicornavirus agent with potent in vitro activity against both group A and group B rhinovirus serotypes. Although its predecessor, R 61837, a substituted phenyl-pyridazinamine, was effective in inhibiting 80% of 100 serotypes tested (EC80) at concentrations above 32 micrograms/ml, pirodavir inhibits the same percentage of viruses at 0.064 micrograms/ml. Pirodavir was one of the most promising capsid-binding compounds to show efficacy in human clinical trials for chemoprophylaxis of the common cold. Kinase Assay: Pirodavir is a potent, broad-spectrum picornavirus inhibitor. Pirodavir inhibits 80 of the 100 human rhinovirus (HRV) strains tested at a concentration of 64 ng/mL. In that same study, Pirodavir is also effective in inhibiting 16 enteroviruses, with a mean 80% inhibitory concentration (IC80) of 1,300 ng/mL. Pirodavir inhibits enterovirus 71 replication with an IC50 of 5,420 nM and an IC90 of >13,350 nM. Pirodavir inhibits 56 rhinovirus laboratory strains and three of the clinical isolates tested. Pirodavir inhibits 59% of the serotypes and isolates with IC50s of<100 16='' nm.='' pirodavir='' concentrations='' of='' and='' ml='' reduces='' cell='' growth='' by='' s.e.m.='' respectively.='' lower='' are='' not='' inhibitory='' for='' growth.='' the='' cytotoxic='' concentration='' logarithmic='' at='' c='' is='' ml.='' under='' conditions='' antiviral='' assay='' confluent='' hela='' cells=''>50μg/mL. Cell Assay: HeLa cells are seeded at a concentration of approximately 180,000 cells per dish in six-well plates containing 4 mL of growth medium. Growth medium consist of Eagle's basal medium, supplemented with 5% fetal calf serum, 2% sodium bicarbonate, and 1% glutamine. After 24 h of incubation at 37°C in a humidified CO2 atmosphere, the growth medium is removed and replaced by the test solutions (fresh growth medium with or without various concentrations of the antiviral compounds). To assess the cytotoxicity of the antiviral compounds (e.g., Pirodavir), the number of living cells are determined present in triplicate cultures at the time of Pirodavir addition and every 24 h for 3 days. Following trypsinization, the number of viable cells for each drug concentration is counted in triplicate with a Coulter Counter. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.7067 mL | 13.5333 mL | 27.0665 mL | 54.1331 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5413 mL | 2.7067 mL | 5.4133 mL | 10.8266 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2707 mL | 1.3533 mL | 2.7067 mL | 5.4133 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1353 mL | 0.6767 mL | 1.3533 mL | 2.7067 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































