NSC 16590
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100g | $450 | To Be Confirmed |
| 200g | $700 | To Be Confirmed |
| 500g | $1180 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V5037 CAS #: 62-57-7 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: NSC 16590 is a novel biochemical that inhibits the production of endogenous ethylene in the cotyledonary segments of cocklebur.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 103.12 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₄H₉NO₂ |
| CAS No. | 62-57-7 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
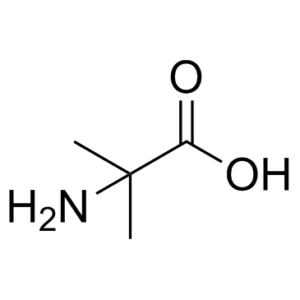
| SMILES Code | NC(C)(C)C(O)=O |
| Synonyms | NSC 16590; NSC-16590 ; NSC16590 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | NSC 16590 (α-Aminoisobutyric acid , AIB) inhibits the production of endogenous ethylene in the cotyledonary segments of cocklebur (Xanthium pennsylvanicum Wallr.) seeds most strongly. NSC 16590 at 4 mM inhibits the formation of ethylene by about 50%, although the O2 uptake of the segments is not affected even at 20 mM. NSC 16590 also inhibits ethylene formation in the stem segments of etiolated pea (Pisum satiuum L. cv. Alaska) seedlings. Kinetic analysis with cell free extracts from etiolated pea shoots reveals that NSC 16590 competitively inhibits the conversion of ACC into ethyle. |
|---|
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 9.6974 mL | 48.4872 mL | 96.9744 mL | 193.9488 mL |
| 5mM | 1.9395 mL | 9.6974 mL | 19.3949 mL | 38.7898 mL |
| 10mM | 0.9697 mL | 4.8487 mL | 9.6974 mL | 19.3949 mL |
| 20mM | 0.4849 mL | 2.4244 mL | 4.8487 mL | 9.6974 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































