This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $750 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1250 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1875 | Check With Us |
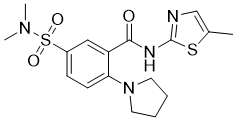
Cat #: V3753 CAS #: 790702-57-7 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: ML414 (also known NGI-1) is a novel and cell-permeable inhibitor of oligosaccharyltransferase (OST), which is a hetero-oligomeric enzyme that exists in multiple isoforms and transfers oligosaccharides to recipient proteins. ML414 was identified from a cell-based high-throughput screen and lead-compound-optimization campaign. In non-small-cell lung cancer cells, NGI-1 blocks cell-surface localization and signaling of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) glycoprotein, but selectively arrests proliferation in only those cell lines that are dependent on EGFR (or fibroblast growth factor, FGFR) for survival. In these cell lines, OST inhibition causes cell-cycle arrest accompanied by induction of p21, autofluorescence, and cell morphology changes, all hallmarks of senescence. These results identify OST inhibition as a potential therapeutic approach for treating receptor-tyrosine-kinase-dependent tumors and provides a chemical probe for reversibly regulating N-linked glycosylation in mammalian cells.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 394.51 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H22N4O3S2 |
| CAS No. | 790702-57-7 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Synonyms | ML414; ML 414; ML-414; NGI-1; NGI1; NGI 1 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: ML414 (also known NGI-1) is a novel and cell-permeable inhibitor of oligosaccharyltransferase (OST), which is a hetero-oligomeric enzyme that exists in multiple isoforms and transfers oligosaccharides to recipient proteins. ML414 was identified from a cell-based high-throughput screen and lead-compound-optimization campaign. In non-small-cell lung cancer cells, NGI-1 blocks cell-surface localization and signaling of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) glycoprotein, but selectively arrests proliferation in only those cell lines that are dependent on EGFR (or fibroblast growth factor, FGFR) for survival. In these cell lines, OST inhibition causes cell-cycle arrest accompanied by induction of p21, autofluorescence, and cell morphology changes, all hallmarks of senescence. These results identify OST inhibition as a potential therapeutic approach for treating receptor-tyrosine-kinase-dependent tumors and provides a chemical probe for reversibly regulating N-linked glycosylation in mammalian cells. Kinase Assay: The HTS approach using the bioluminescent N-linked glycosylation reporter in D54-ERLucT and D54-LucT cells has been previously described. Briefly, the primary cell-based screen detects N-linked glycan site occupancy using a modified and ER translated luciferase protein with three N-linked glycosylation consensus sequons. Inhibition of glycosylation in D54-ERLucT restores and increases luciferase activity over controls whereas it does not increase activity in the non-ER translated D54-LucT cell line. The methodology for the primary (D54-ERlucT), secondary false positive (D54-LucT), and tertiary (luciferase inhibition) screens as well as toxicity assays with CellTitre Glo are deposited in Pubchem (AID 588693). Genedata Screener software with the Smartfit algorithm was used for to generate AC40 values for comparative analysis of analogs. Cell Assay: In non-small-cell lung cancer cells, NGI-1 blocks cell-surface localization and signaling of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) glycoprotein, but selectively arrests proliferation in only those cell lines that are dependent on EGFR (or fibroblast growth factor, FGFR) for survival. In these cell lines, OST inhibition causes cell-cycle arrest accompanied by induction of p21, autofluorescence, and cell morphology changes, all hallmarks of senescence. These results identify OST inhibition as a potential therapeutic approach for treating receptor-tyrosine-kinase-dependent tumors and provides a chemical probe for reversibly regulating N-linked glycosylation in mammalian cells. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.5348 mL | 12.6739 mL | 25.3479 mL | 50.6958 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5070 mL | 2.5348 mL | 5.0696 mL | 10.1392 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2535 mL | 1.2674 mL | 2.5348 mL | 5.0696 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1267 mL | 0.6337 mL | 1.2674 mL | 2.5348 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































