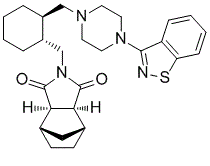
Lurasidone
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 10g | $450 | Check With Us |
| 25g | $800 | Check With Us |
| 50g | $1200 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V23782 CAS #: 367514-87-2 Purity ≥ 99%
Description: Lurasidone (SM13496; SM-13496; Latuda) is an atypical antipsychotic drug approved for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorders.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 492.68 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H36N4O2S |
| CAS No. | 367514-87-2 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Lurasidone (SM-13496) is an antagonist of dopamine D2 and 5-HT7 with IC50s of 1.68±0.09 and 0.495±0.090 nM, respectively. Lurasidone (SM-13496) is also a partial agonist of 5-HT1A receptor with an IC50 of 6.75±0.97 nM. In vitro receptor binding experiments reveal that Lurasidone (SM-13496) demonstrates affinity for dopamine D2 and 5-HT2A receptors higher than other tested antipsychotics. Lurasidone (SM-13496) does not increase [35S]GTPγS binding to the membrane preparations for dopamine D2 receptors by itself, but it antagonizes dopamine-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in a concentration-dependent manner with a KB value of 2.8±1.1 nM |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Lurasidone (SM-13496) dose-dependently increases the ratio of DOPAC/dopamine in frontal cortex and striatum, but it shows a preferential effect on the frontal cortex compare with the striatum, especially at higher doses. Lurasidone (SM-13496) (ED50 values 2.3 to 5.0 mg/kg) shows a comparable potency with olanzapine (ED50 values 1.1 to 5.1 mg/kg), higher potency than clozapine (ED50 9.5 to 290 mg/kg), and slightly lower potency than haloperidol (ED50 values 0.44 to 1.7 mg/kg). Lurasidone (SM-13496) (1 to 10 mg/kg) dose-dependently inhibits conditioned avoidance response (CAR) in rats, and the ED50 values are 6.3 mg/kg. Lurasidone (SM-13496) dose-dependently inhibits tryptamine (TRY)-induced forepaw clonic seizure and p-chloroamphetamine (p-CAMP)-induced hyperthermia with ED50 values of 5.6 and 3.0 mg/kg, respectively. Lurasidone (SM-13496) (0.3 to 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently and significantly increases the number of shocks received by rats in the conflict test with MED of 10 mg/kg (p<0.01) |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.0297 mL | 10.1486 mL | 20.2972 mL | 40.5943 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4059 mL | 2.0297 mL | 4.0594 mL | 8.1189 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2030 mL | 1.0149 mL | 2.0297 mL | 4.0594 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1015 mL | 0.5074 mL | 1.0149 mL | 2.0297 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































