This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5mg | $195 | To Be Confirmed |
| 10mg | $235 | To Be Confirmed |
| 25mg | $340 | To Be Confirmed |
| 50mg | $510 | To Be Confirmed |
| 100mg | $769 | To Be Confirmed |
| 250mg | $1340 | To Be Confirmed |
| 500mg | $1950 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V3040 CAS #: 259869-55-1 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: JWH-133 is a synthetic cannabinoid and a potent & selective agonist of the CB2 receptor with a Ki of 3.4nM and selectivity of ~ 200x for CB2 over CB1 receptors. It was discovered by and named after, John W. Huffman. JWH-133 is responsible for preventing the inflammation caused by Amyloid beta proteins involved in Alzheimer's Disease, in addition to preventing cognitive impairment and loss of neuronal markers. This anti-inflammatory action is induced through agonist action at cannabinoid receptors, which prevents microglial activation that elicits the inflammation. Additionally, cannabinoids completely abolish neurotoxicity related to microglia activation in rat models. It may also have anticancer activities.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 312.50 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H32O |
| CAS No. | 259869-55-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mM |
| Water: <1 mg/mL | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
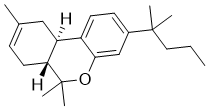
| SMILES Code | CC(C1)=CC[C@]2([H])[C@]1([H])C3=CC=C(C(C)(C)CCC)C=C3OC2(C)C |
| Synonyms | JWH133; JWH-133; JWH133 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: JWH-133 is a synthetic cannabinoid and a potent & selective agonist of the CB2 receptor with a Ki of 3.4nM and selectivity of ~ 200x for CB2 over CB1 receptors. It was discovered by and named after, John W. Huffman. JWH-133 is responsible for preventing the inflammation caused by Amyloid beta proteins involved in Alzheimer's Disease, in addition to preventing cognitive impairment and loss of neuronal markers. This anti-inflammatory action is induced through agonist action at cannabinoid receptors, which prevents microglial activation that elicits the inflammation. Additionally, cannabinoids completely abolish neurotoxicity related to microglia activation in rat models. It may also have anticancer activities. Kinase Assay: JWH-133 evoked a concentration-related inhibition (10 nM-5 microM) of LPS/IFN-gamma induced IL-12p40 release. The effect of JWH-133 (100 nM) was significantly blocked by the CB2 antagonist SR-144528 (1 microM). Macrophages infected with TMEV increased IL-12p40 production and activation of CB2 receptors by JWH-133 (100 nM) inhibited it. The inhibitory effect of JWH-133 (100 nM) on IL-12p40 production may involve extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) signaling: (i) JWH-133 induced a greater and sustained activation of ERK1/2 kinase in comparison with the level of activation observed following LPS; (ii) the inhibition of ERK1/2 by the specific inhibitor PD98059 increased LPS-induced IL-12p40 production in the presence or absence of JWH-133 suggesting a negative regulation of ERK pathway on IL-12p40 biosynthesis. Cell Assay: Activation of CB2 receptors by JWH-133 (10 nM-5 microM) enhanced IL-10 release by LPS/IFN-gamma-activated macrophages and addition of SR144558 (1 microM) totally blocked the effect of JWH (100 nM). 5 Inhibition of ERK by PD98059 significantly suppressed IL-10 production by LPS-activated macrophages. Endogenous IL-10 plays a modulatory role in IL-12 production. Blocking IL-10 with neutralizing antibody resulted in increased IL-12p40 secretion by LPS-activated macrophages in the absence or presence of JWH-133. In contrast, the addition of exogenous mIL-10 reduced the secretion of IL-12p40 in response to LPS. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.2000 mL | 16.0000 mL | 32.0000 mL | 64.0000 mL |
| 5mM | 0.6400 mL | 3.2000 mL | 6.4000 mL | 12.8000 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3200 mL | 1.6000 mL | 3.2000 mL | 6.4000 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1600 mL | 0.8000 mL | 1.6000 mL | 3.2000 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































