This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $550 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $850 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $2150 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V21222 CAS #: 863971-53-3 Purity ≥ 98%
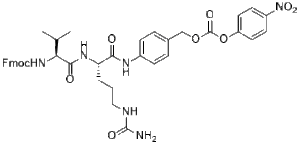
Description: Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP is a linker for Antibody-Drug-Conjugation (ADC). The Val-Cit will specifically be cleaved by catepsin B. Because this enzyme is only present in the lysosome, the ADC payload will only be released in the cell. The azido group will react with DBCO, BCN or other alkyne groups through click chemistry. The hydrophilic PEG spacer increases solubility in aqueous media.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 766.80 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C40H42N6O10 |
| CAS No. | 863971-53-3 |
| SMILES Code | O=C(OCC1=CC=C(NC([C@H](CCCNC(N)=O)NC([C@H](C(C)C)NC(OCC2C(C=CC=C3)=C3C4=C2C=CC=C4)=O)=O)=O)C=C1)OC5=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C5 |
| Synonyms | Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP contains peptide sequence degradable by a lysosome enzyme. Cathepsin B in the lysosome cleaves the peptide bond between Cit-PAB of dipeptide linkers containing Valine (Val)-citrulline (Cit) and p-aminobenzylalcohol (PAB). When PAB and a drug are binded covalently with carbamate bonds, the drug can be released by hydrolysis after cleavage of the peptide bond between Cit-PAB. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) has been developed using this mechanism. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB-PNP linker stabilization in the mouse is an essential prerequisite for designing successful efficacy and safety studies in rodents during preclinical stages of ADC programs. Conjugation site plays an important role in determining VC-PABC linker stability in mouse plasma, and that the stability of the linker positively correlates with ADC cytotoxic potency both in vitro and in vivo. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.3041 mL | 6.5206 mL | 13.0412 mL | 26.0824 mL |
| 5mM | 0.2608 mL | 1.3041 mL | 2.6082 mL | 5.2165 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1304 mL | 0.6521 mL | 1.3041 mL | 2.6082 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0652 mL | 0.3260 mL | 0.6521 mL | 1.3041 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































