This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $600 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $950 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1425 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3511 CAS #: 142217-69-4 Purity ≥ 98%
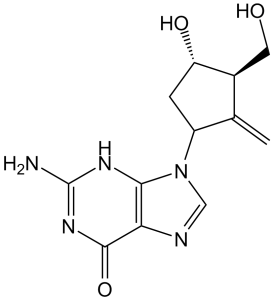
Description: Entecavir (Baraclude; SQ34676 and BMS200475), anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) agent, is a novel deoxyguanine nucleoside analogue and a reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Entecavir is a potent and selective inhibitor of HBV, with an EC50 of 3.75 nM in HepG2 cells. It is an oral antiviral drug used in the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. It prevents the hepatitis B virus from multiplying and reduces the amount of virus in the body. Entecavir is a highly potent inhibitor of wild-type HBV Pol and is 100- to 300-fold more potent than lamivudine-triphosphate against 3TC-resistant HBV Pol. Entecavir inhibits the replication of 3TC-resistant HBV, but 20- to 30-fold higher concentrations are required.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 277.28 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H15N5O3 |
| CAS No. | 142217-69-4 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >40 mg/mLr |
| Water:<1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol:<1 mg/mL | |
| SMILES Code | O=C1NC(N)=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]3C([C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)C3)=C.[H]O[H] |
| Synonyms | BMS 200475-01; BMS-200475; BMS 200475; Baraclude; BMS200475; BMS-200475-01; Entecavir monohydrate; D07896 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Entecavir-triphosphate is a highly potent inhibitor of wild-type HBV Pol and is 100- to 300-fold more potent than lamivudine-triphosphate against 3TC-resistant HBV Pol. Entecavir inhibits the replication of 3TC-resistant HBV, but 20- to 30-fold higher concentrations are required. Entecavir results in an impressive reduction of serum viral DNA with covalently closed circular DNA and hepatitis B viral core antigen negativity in liver biopsy specimens. Entecavir has potent activity (EC50, 0.1 nM) against HIV in a unique single-cycle, single-cell-based pseudovirus assay (24) with CD4+ lymphocytes using a green fluorescent protein reporter fluorescence-activated cell sorter assay as the endpoint. Kinase Assay: BMS-200475 has a EC50 of 3.75 nM against HBV. It is incorporated into the protein primer of HBV and subsequently inhibits the priming step of the reverse transcriptase. The antiviral activity of BMS-200475 is significantly less against the other RNA and DNA viruses. Entecavir is more readily phosphorylated to its active metabolites than other deoxyguanosine analogs (penciclovir, ganciclovir, lobucavir, and aciclovir) or lamivudine. The intracellular half-life of entecavir is 15 h. Cell Assay: BMS 200475 is prepared in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and diluted with appropriate medium containing 2% fetal bovine serum. HepG2 2.2.15 cells are plated at a density of 5×105 cells per well on 12-well Biocoat collagen-coated plates and are maintained in a confluent state for 2 to 3 days before being overlaid with 1 mL of medium spiked with BMS 200475. Quantification of HBV was performed on day 10. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Entecavir causes a 4-log drop in serum DHBV DNA levels within 80 days and a slower 2- to 3-log drop in serum DHBV surface antigen (DHBsAg) levels within 120 days in ducks. Entecavir treatment reduces DHBV DNA replicative intermediates 70-fold in the liver, while the level of the stable, template form, covalently closed circular DNA decreases only 4-fold in ducks. Entecavir treatment reduces both the intensity of antigen staining and the percentage of antigen-positive hepatocytes in the liver, but the intensity of antigen staining in bile duct cells appeares not to be effected in ducks. Daily oral treatment with BMS-200475 at doses ranging from 0.02 to 0.5 mg/kg of body weight for 1 to 3 months effectively reduces the level of woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) viremia in chronically infected woodchucks | |
| Animal model | Ducks and Wookchucks | |
| Dosages | 0.02 to 0.5 mg/kg | |
| Administration | oral |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.6065 mL | 18.0323 mL | 36.0646 mL | 72.1293 mL |
| 5mM | 0.7213 mL | 3.6065 mL | 7.2129 mL | 14.4259 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3606 mL | 1.8032 mL | 3.6065 mL | 7.2129 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1803 mL | 0.9016 mL | 1.8032 mL | 3.6065 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































