This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 2g | $180 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $300 | Check With Us |
| 10g | $450 | Check With Us |
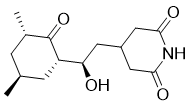
Cat #: V3042 CAS #: 66-81-9 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Cycloheximide, produced by S. griseus, is a glutarimide antibiotic and an inhibitor of protein synthesis in eukaryotes (but not prokaryotes) with IC50 of 5-50 μM (IC50s of 532.5 nM and 2880 nM for protein synthesis and RNA synthesis in vivo, respectively).
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 281.35 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H23NO4 |
| CAS No. | 66-81-9 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >14.1mg/mLr |
| Water: <1mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol:<1mg/mL | |
| Synonyms | Naramycin A; Actidione; Cycloheximide; NSC 185 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Cycloheximide (CHX) is the most common laboratory reagent used to inhibit protein synthesis. Cycloheximide has been shown to block the elongation phase of eukaryotic translation. Cycloheximide binds the ribosome and inhibits eEF2-mediated translocation. Surprisingly, Cycloheximide allows one complete translocation cycle to proceed before halting any further elongation. Cycloheximide has been speculated that Cycloheximide requires an E-site bound deacylated tRNA for activity |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.5543 mL | 17.7715 mL | 35.5429 mL | 71.0858 mL |
| 5mM | 0.7109 mL | 3.5543 mL | 7.1086 mL | 14.2172 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3554 mL | 1.7771 mL | 3.5543 mL | 7.1086 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1777 mL | 0.8886 mL | 1.7771 mL | 3.5543 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































