This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5mg | $150 | To Be Confirmed |
| 10mg | $250 | To Be Confirmed |
| 25mg | $450 | To Be Confirmed |
| 50mg | $680 | To Be Confirmed |
| 100mg | $1050 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V3271 CAS #: 1345810-21-0 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: CB-1158 analog (CB-1158, INCB01158 or Numidargistat analog) is a potent and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of the arginase with potential immunomodulating activities. Myeloid cells are an abundant leukocyte in many types of tumors and contribute to immune evasion. Expression of the enzyme arginase 1 (Arg1) is a defining feature of immunosuppressive myeloid cells and leads to depletion of L-arginine, a nutrient required for T cell and natural killer (NK) cell proliferation. CB-1158 has shown high anti-cancer activity in renal cell cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, and other tumor types where arginase-secreting MDSCs are known to play an immunosuppressive role. Arginase blockade by CB-1158 may be an effective therapy in multiple types of cancer, also the combination of CB-1158 with standard-of-care chemotherapy or other immunotherapies that target T-cell activation, such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies may yield improved clinical responses. CB-1158 is currently in a Phase I clinical trial as a single agent and in combination with immune checkpoint therapy in patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 417.13 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H27BCl2N2O4 |
| CAS No. | 1345810-21-0 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: > 10mM |
| Water: N/A | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
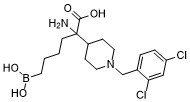
| SMILES Code | ClC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1CN2CCC(C(N)(CCCCB(O)O)C(O)=O)CC2 |
| Synonyms | INCB01158, CB-1158, INCB 01158, CB 1158, INCB-01158; CB1158 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: CB-1158 (previously known as INCB01158) is a potent and orally-bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of the arginase. Myeloid cells are an abundant leukocyte in many types of tumors and contribute to immune evasion. Expression of the enzyme arginase 1 (Arg1) is a defining feature of immunosuppressive myeloid cells and leads to depletion of L-arginine, a nutrient required for T cell and natural killer (NK) cell proliferation. CB-1158 has shown high anti-cancer activity in renal cell cancer, breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, and other tumor types where arginase-secreting MDSCs are known to play an immunosuppressive role. Arginase blockade by CB-1158 may be an effective therapy in multiple types of cancer, also the combination of CB-1158 with standard-of-care chemotherapy or other immunotherapies that target T-cell activation, such as CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies may yield improved clinical responses. Kinase Assay: Recombinant human arginase 2 (Arg2) comprising amino acids 23–254 was purchased from US Biological (Salem, MA). Activity assays using 2 nM Arg1 or 4 nM Arg2 were performed in reaction buffer (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 8 mM Na2HPO4, 2 mM KH2PO4, 0.005% Triton X-100, 0.5 mM DTT, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM CaCl2, and 160 μM or 20 mM L-arginine, pH 7.4) at 37 °C for 30 min with a dose-titration of CB-1158. Activity was determined by a spectrophotometric assay using the QuantiChrom Urea Assay Kit (BioAssay Systems, Hayward, CA) or by quantification of the generation of 13C(5)-L-ornithine from 13C(6)-L-arginine using a SCIEX API4000 mass spectrometer. Urea produced or 13C(5)-L-ornithine peak areas were plotted and fitted to a four-parameter equation using GraphPad Prism software (San Diego, CA) to determine IC50 values. Cell Assay: T cells or NK cells were purified from healthy donor human blood or from murine splenocytes using a negative selection kit for the appropriate cell type and species from Stemcell Technologies. Isolated T cells or NK cells were loaded with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE, Thermo Fisher) and stimulated for 72–96 h in complete growth medium containing a minimum of either 50 μM L-arginine (NK cells) or 100 μM L-arginine (T cells). For T cell stimulation, a solution of 10 μg/mL anti-CD3 (human clones UCHT1 or OKT3; murine clone 145-2C11) was used to coat the wells of a 96-well plate and then T cells were stimulated on immobilized anti-CD3 in the presence of 2 μg/mL soluble anti-CD28 (human clone CD28.2; murine clone 37.51). NK cells were stimulated with recombinant IL-2. Proliferation was quantified by analyzing CFSE dilution by flow cytometry. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Female wild-type C57BL/6 and Balb/c mice (5–6 weeks old) were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Hollister, CA). Severe combined immune deficient (SCID, B6.CB17-PrkdcSCID/SzJ) and Pmel-1 TCR transgenic (B6.Cg-Thy1a/Cy Tg(TcraTcrb)8Rest/J) mice (5–6 weeks old) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). All mice were housed and treated in accordance with Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines. For the 4T1 tumor model, 105 cells were injected orthotopically into the mammary fat pad; for all other tumor models, 106 cells were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) in the right flank. For all studies, CB-1158 was administered by oral gavage twice per day at 100 mg/kg starting on study day 1 (1 day after tumor implant). Control groups received vehicle (water) twice daily by gavage. Tumor volume measured by digital caliper (length × width × width/2) and body weight were recorded three times per week. Animals were euthanized when tumors necrotized or volumes reached 2000 mm3. For the CT26 model, anti-PD-L1 antibody (5 mg/kg, clone 10F.9G2, BioXCell, West Lebanon, NH) was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) on days 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15. For the 4T1 model, anti-CTLA-4 antibody (5 mg/kg, clone 9H10, BioXCell) was injected i.p. on days 2, 5, and 8; anti-PD-1 antibody (5 mg/kg, clone RMP1–14, BioXCell) was injected i.p. on days 3, 6, and 9. 4T1 tumors were harvested on study day 25 into Fekete’s solution and tumor nodules were enumerated visually. Gemcitabine was dosed 50 mg/kg i.p. on days 10 and 16 for the CT26 model, 60 mg/kg i.p. on days 6 and 10 for the LLC model, or 30 mg/kg i.p. on day 5 for the 4T1 model. With these regimens, gemcitabine modestly reduces tumor growth and spares most tumor-infiltrating immune cells, allowing for the evaluation of combination activity with CB-1158. For CD8+ cell depletion, mice were injected i.p. with anti-CD8 antibody (25 mg/kg, clone 2.43, BioXCell) on days −1, 0, + 5, and +10. For NK cell depletion, mice were injected i.p. with anti-NK1.1 antibody (25 mg/kg, clone PK136, BioXCell) in the LLC and B16 models or with anti-Asialo GM1 sera (20 μL) in the CT26 model, per the same schedule as anti-CD8. | |
| Animal model | Female wild-type C57BL/6 and Balb/c mice (5–6 weeks old) |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.3973 mL | 11.9867 mL | 23.9733 mL | 47.9467 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4795 mL | 2.3973 mL | 4.7947 mL | 9.5893 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2397 mL | 1.1987 mL | 2.3973 mL | 4.7947 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1199 mL | 0.5993 mL | 1.1987 mL | 2.3973 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































