Abscisic Acid (Dormin)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $850 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1350 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2025 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V1906 CAS #: 21293-29-8 Purity ≥ 98%
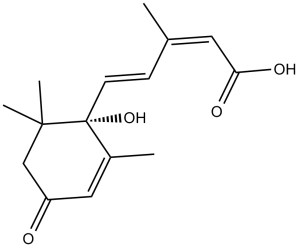
Description: Abscisic Acid (also known as ABA, and Abscisin II) is a plant hormone and growth inhibitor, which is involved in many plant developmental processes, modulates ion homeostasis and metabolism, and inhibits germination and seedling growth.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 264.32 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H20O4 |
| CAS No. | 21293-29-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 52 mg/mL (196.7 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: 52 mg/mL (196.7 mM) | |
| SMILES Code | O=C(O)/C=C(C)\C=C\[C@@]1(O)C(C)=CC(CC1(C)C)=O |
| Synonyms | Abscisin II; (S)-(+)-Abscisic acid; ABA |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Abscisic acid (10 μM) increases Ca2+ in cytosol of Arabidopsis cell suspension. Abscisic acid does not inhibit proton pumping directly but through an increase in cytosolic Ca2+. In Arabidopsis cell cultures, Abscisic acid ((S)-(+)-Abscisic acid; 10 μM) simultaneously induces rapid alkalinization of the medium and plasma membrane depolarization. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Abscisic acid (orally; 0.125 µg/kg/day; for 12 weeks) improves glycemic control. |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.7833 mL | 18.9165 mL | 37.8329 mL | 75.6659 mL |
| 5mM | 0.7567 mL | 3.7833 mL | 7.5666 mL | 15.1332 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3783 mL | 1.8916 mL | 3.7833 mL | 7.5666 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1892 mL | 0.9458 mL | 1.8916 mL | 3.7833 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































