This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $1150 | Check With Us |
| 250mg | $1950 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $2925 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3189 CAS #: 1572510-80-5 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: AB-423, a member of the sulfamoylbenzamide (SBA) class, is a potent HBV (hepatitis B virus) capsid assembly inhibitor that inhibits HBV replication with EC50/EC90 of 0.08-0.27 μM/0.33-1.32 μM in cells. AB-423 is currently under phase 1 clinical trials. AB-423 inhibited HBV genotypes A through D and nucleos(t)ide-resistant variants in vitro Treatment of HepDES19 cells with AB-423 resulted in capsid particles devoid of encapsidated pregenomic RNA and relaxed circular DNA (rcDNA), indicating that it is a class II capsid inhibitor. In a de novo infection model, AB-423 prevented the conversion of encapsidated rcDNA to covalently closed circular DNA, presumably by interfering with the capsid uncoating process. Molecular docking of AB-423 into crystal structures of heteroaryldihydropyrimidines and an SBA and biochemical studies suggest that AB-423 likely also binds to the dimer-dimer interface of core protein.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 386.39 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₁₇H₁₇F₃N₂O₃S |
| CAS No. | 1572510-80-5 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >80 mg/mLr |
| Water:r | |
| Ethanol: | |
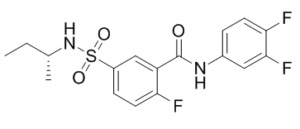
| SMILES Code | O=C(NC1=CC=C(F)C(F)=C1)C2=CC(S(=O)(N[C@H](C)CC)=O)=CC=C2F |
| Synonyms | AB 423; AB423 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: AB-423 is a potent inhibitor of HBV capsid assembly that shows inhibitory effect on rcDNA production in AML12-HBV10 and HepDE19 cells with EC50s of ∼0.260 μM. AB-423 also suppresses cccDNA formation-dependent HBeAg production in the HepBHAe82 assay with an EC50 of 0.267 μM and inhibits HBV DNA levels in culture supernatants of HepG 2.2.15 cells with an EC50 of 0.134 μM. However, AB-423 has no cytotoxicity in any of the three cell lines. Kinase Assay: Cell Assay: HepBHAe82 (50,000 cells/well) are plated in 96-well tissue-culture treated microtiter plates in DMEM/F12 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin-streptomycin and tetracycline (1 μg/mL), and incubated in a humidified incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2 overnight. On the next day, the cells are switched to fresh medium and treated with inhibitor A and inhibitor B, at concentration range in the vicinity of their respective EC50 values. The inhibitors are either diluted in 100% DMSO (ETV, TDF and AB-423) or growth medium (ARB-1467 and ARB-1740) and the final DMSO concentration in the assay is ≤0.5%. The two inhibitors are tested both singly as well as in combinations determine their effects on inhibition of rcDNA production. The final DMSO concentration in the assay is 0.5%. The plates are incubated for 9 days in a humidified incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2. Following a 9 day-incubation, medium is removed, and cells are subjected to RNA extraction to measure the cccDNA-dependent precore mRNA leve |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | AB-423 (30 and 100 mg/kg, p.o. bid) inhibits HBV replication in a mouse model of HBV. AB-423 (100 mg/kg, p.o. bid) with entecavir (ETV, 100 ng/mg, qd, p.o.) or 0.1 mg/kg dose of ARB-1467 potently inhibits serum HBV DNA in an HDI model of HBV in immunodeficient NOD-SCID mice. | |
| Animal model | NOD-SCID mice | |
| Dosages | 30 and 100 mg/kg | |
| Administration | p.o. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.5881 mL | 12.9403 mL | 25.8806 mL | 51.7612 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5176 mL | 2.5881 mL | 5.1761 mL | 10.3522 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2588 mL | 1.2940 mL | 2.5881 mL | 5.1761 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1294 mL | 0.6470 mL | 1.2940 mL | 2.5881 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































