This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
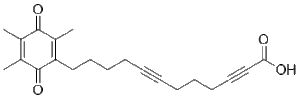
Cat #: V3064 CAS #: 90316-11-3 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: A1777 is a novel, potent and selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor that can reduce proliferation of leukocytes without affecting the eosinophils of mast cells. 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) catalyzes two steps in biosynthesis of leukotrienes (LTs), a group of lipid mediators of inflammation derived from arachidonic acid (AA). LT antagonists are used in treatment of asthma; more recently a potential role also in atherosclerosis has raised considerable interest. In IgG-BSA complex pleurisy, 90% of the pleural exudate for the first 20 minutes was inhibited by the same treatment, and the rest was completely suppressed by simultaneous treatment with an intrapleural injection of AA-1777. AA-1777 was also very effective in reducing the migrating numbers of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes to half.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 340.42 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H24O4 |
| CAS No. | 90316-11-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mM |
| Water: N/A | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Synonyms | AA1777; AA 1777; AA-1777 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: A1777 is a novel, potent and selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor that can reduce proliferation of leukocytes without affecting the eosinophils of mast cells. 5-Lipoxygenase (5-LO) catalyzes two steps in biosynthesis of leukotrienes (LTs), a group of lipid mediators of inflammation derived from arachidonic acid (AA). LT antagonists are used in treatment of asthma; more recently a potential role also in atherosclerosis has raised considerable interest. In IgG-BSA complex pleurisy, 90% of the pleural exudate for the first 20 minutes was inhibited by the same treatment, and the rest was completely suppressed by simultaneous treatment with an intrapleural injection of AA-1777. AA-1777 was also very effective in reducing the migrating numbers of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes to half. Kinase Assay: Cell Assay: In IgG-BSA complex pleurisy, 90% of the pleural exudate for the first 20 minutes was inhibited by the same treatment, and the rest was completely suppressed by simultaneous treatment with an intrapleural injection of AA-1777. AA-1777 was also very effective in reducing the migrating numbers of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes to half. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Rat IgE pleurisy was induced by the injection of di-nitrophenol-conjugated bovine serum albumin (DNP-BSA) 48 hours after the intrapleural injection of rat anti-DNP-IgE serum. IgG-BSA complex pleurisy was also induced by the intrapleural injection of IgG-BSA complexes produced at the optimum ratio in vitro. Plasma exudation was markedly increased in the first 20 minutes, but not observed thereafter, in IgE pleurisy, whereas marked plasma exudation in the first 20 minutes was followed by weak exudation at three and five hours in IgG-BSA complex pleurisy. Leukotrienes (LTs) E4 (100 ng/rat), D4 (32) and B4 (16) were detected on HPLC in the pleural exudate in the first 20 minutes of IgG-BSA complex pleurisy, but less (9 ng/rat) LTE4 alone was detected in the five-hour exudate. The first 20-minute pleural exudate contained 13 ng/rat of LTE4 in IgE pleurisy. The plasma was completely inhibited by simultaneous treatment of rats with pyrilamine (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.) and methysergide (3 mg/kg, i.p.), as it was in compound 48/80-induced pleurisy. In IgG-BSA complex pleurisy, 90% of the pleural exudate for the first 20 minutes was inhibited by the same treatment, and the rest was completely suppressed by simultaneous treatment with an intrapleural injection of AA-1777, a selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. AA-1777 alone did not reduce the plasma exudation significantly. The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor was also very effective in reducing the migrating numbers of polymorphonuclear and mononuclear leukocytes to half, without affecting the eosinophils of mast cells. | |
| Animal model | Rat |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.9375 mL | 14.6877 mL | 29.3755 mL | 58.7510 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5875 mL | 2.9375 mL | 5.8751 mL | 11.7502 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2938 mL | 1.4688 mL | 2.9375 mL | 5.8751 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1469 mL | 0.7344 mL | 1.4688 mL | 2.9375 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































