Sulforaphane (BroccoPhane; Detoxophane)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 1g | $800 | Check With Us |
| 2g | $1350 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $2275 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V10659 CAS #: 4478-93-7 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Sulforaphane (BroccoPhane; Detoxophane) is a naturally-occurring isothiocyanate widely found in consumed vegetables.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | C6H11NOS2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | 177.29 |
| CAS No. | 4478-93-7 |
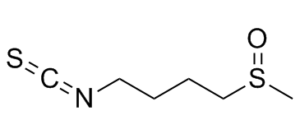
| SMILES Code | O=S(CCCCN=C=S)C |
| Synonyms | Sulforaphane; BroccoPhane; Detoxophane; Sulphoraphane; Broccoli sprout extracts; 4-methyl-sulfinybutyl isothiocyanatel; Sulforafan; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Sulforaphane induces a cell cycle arrest in a dose-dependent manner, followed by cell death. This sulforaphane-induced cell cycle arrest was correlated with an increased expression of cyclins A and B1. Sulforaphane induces cell death via an apoptotic process. Sulforaphane inhibits the reinitiation of growth and diminishes cellular viability in quiescent colon carcinoma cells (HT29) and has a lower toxicity on differentiated CaCo2 cells. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Sulforaphane can block the formation of ammary tumors in Sprague-Dawley rats treated with single doses of 9,10-dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene. Administration of sulforaphane reduces the incidence, multiplicity, and weights and delays the development of the mammary tumors evoked by a single dose of DMBA in female Sprague-Dawley rats. |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































