FX1
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $1125 | In Stock |
| 1g | $1680 | In Stock |
| 5g | $4250 | In Stock |
Cat #: V2774 CAS #: 1426138-42-2 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: FX1 is a potent and specific inhibitor of the BCL6 (B cell lymphoma 6) with an IC50 of approximately 35 μM.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 368.82 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H9ClN2O4S2 |
| CAS No. | 1426138-42-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 73 mg/mL (197.92 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: Insoluble | |
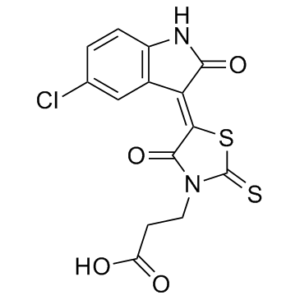
| SMILES Code | O=C(O)CCN(C/1=O)C(SC1=C2C(NC3=C/2C=C(Cl)C=C3)=O)=S |
| Synonyms | FX-1; FX1; FX 1 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | DLBCL cells are exposed to 50 μM FX1 for 30 minutes. FX1 profoundly reduces recruitment of BCOR and SMRT to all 3 BCL6 target genes, but not at a negative control locus. There is little presence of SMRT at these loci in the BCL6-negative DLBCL cell line, which is not affected by FX1. The superior potency of FX1 versus 79-6 in disrupting BCL6 binding to SMRT is evident when these small molecules are compared head to head in quantitative ChIP assays in DLBCL cells after treatment with 50 μM FX1 for 6 hours. DLBCL cells are exposed to FX1 and mRNA is collect at 4 serial time points. FX1 almost invariantly induces significant derepression of these genes as compare with vehicle in 2 independent DLBCL cell lines. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Spleens in FX1-treating mice are macroscopically indistinguishable from vehicle controls. Total B cell abundance measured by flow cytometry is unaffected by FX1. GC B cells (GL7+FAS+B220+) are significantly depleted by exposure to FX1. Splenic architecture is examined by IHC. Staining with B220 antibody reveals normal B cell follicular structures, whereas staining for the GC B cell-specific marker peanut agglutinin shows profound loss of GCs. The half-life is estimated to be approximately 12 hours. Finally, whether FX1 can induce toxic effects in mice is assessed. No signs of toxicity, inflammation, or infection are evident from H&E-stained sections of lung, gastrointestinal tract, heart, kidney, liver, spleen, and bone marrow of the fixed organs from mice treated with FX1 compare with vehicle. |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.7113 mL | 13.5567 mL | 27.1135 mL | 54.2270 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5423 mL | 2.7113 mL | 5.4227 mL | 10.8454 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2711 mL | 1.3557 mL | 2.7113 mL | 5.4227 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1356 mL | 0.6778 mL | 1.3557 mL | 2.7113 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































