This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $750 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1250 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1875 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3715 CAS #: 173903-47-4 Purity ≥ 98%
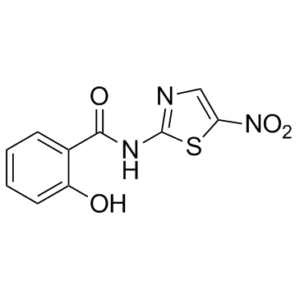
Description: Tizoxanide, a thiazolide anti-infective, is an active metabolite of Nitazoxanide (also known as NTZ; NSC 697855), which is a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative and an antiprotozoal agent with IC50 for canine influenza virus ranges from 0.17 to 0.21 μM. Tizoxanide is active against anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and a range of viruses in cell culture models, and is currently in phase II clinical development for treating chronic hepatitis C.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 265.25 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H7N3O4S |
| CAS No. | 173903-47-4 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 27 mg/mL (101.8 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| SMILES Code | O=C(NC1=NC=C([N+]([O-])=O)S1)C2=CC=CC=C2O |
| Synonyms | Desacetylnitazoxanide; Desacetyl nitazoxanide Desacetyl-nitazoxanide; NSC-697856; NSC697856; NSC697856 |
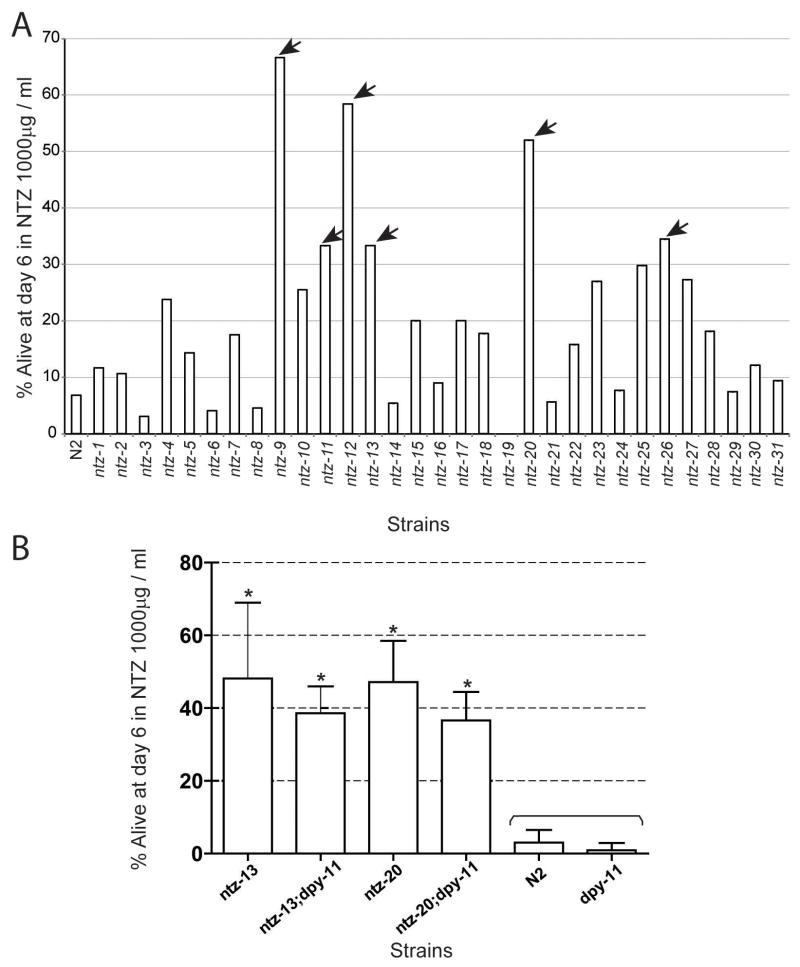
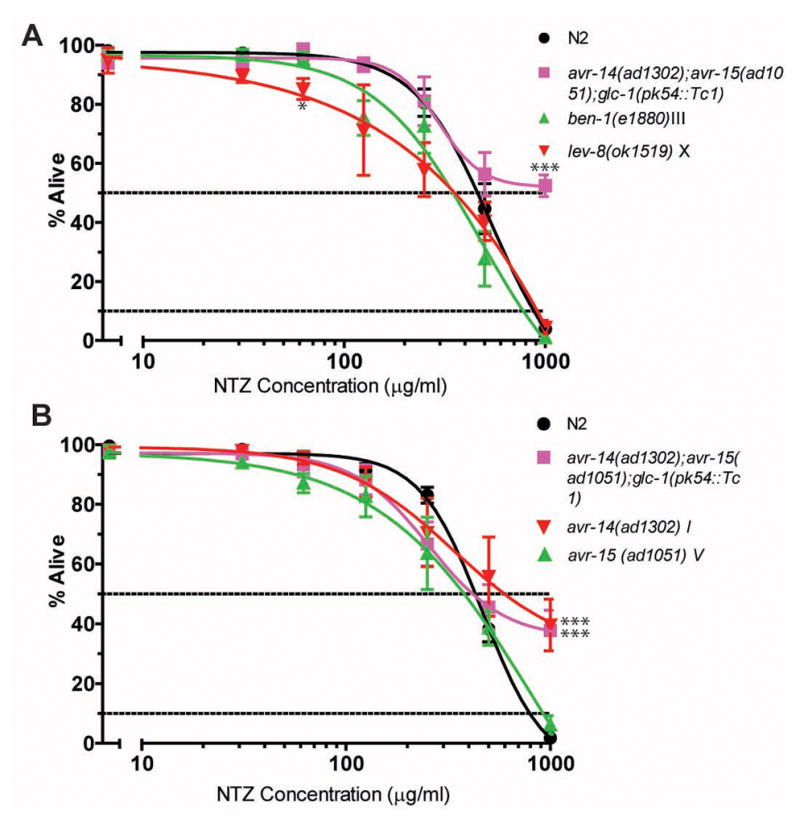
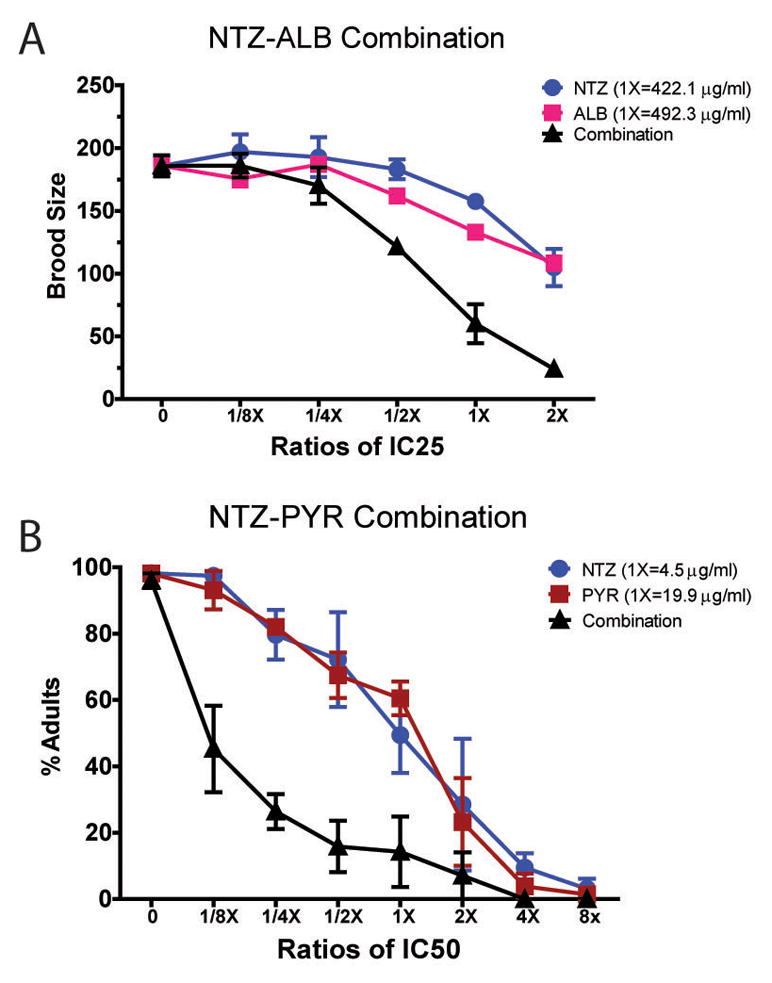
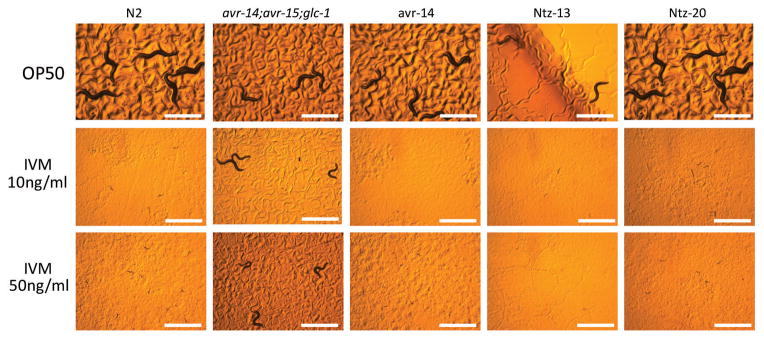
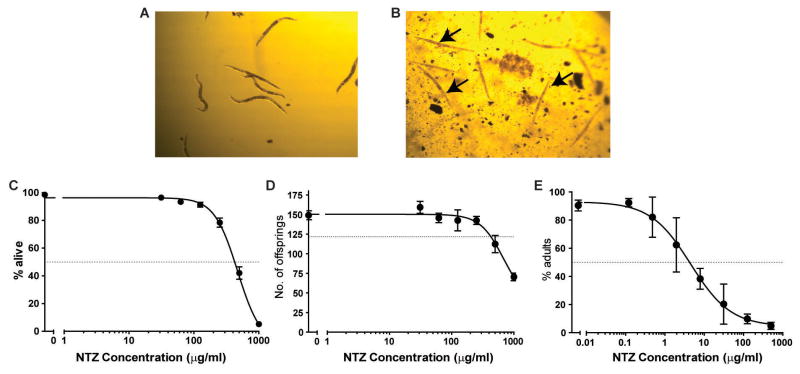
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Tizoxanide is the active metabolite of Nitazoxanide, which is a thiazolide anti-infective compound against anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and a range of viruses. IC50 value: Target: Antiviral agent in vitro: Tizoxanide inhibited virus replication of all CIVs with 50% and 90% inhibitory concentrations ranging from 0.17 to 0.21 μM and from 0.60 to 0.76 μM, respectively. Nitazoxanide and its primary metabolite, tizoxanide, inhibit hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication in HCV replicon systems. Interestingly, serial passage in nitazoxanide or tizoxanide resulted in increased sensitivity to alpha interferon 2b: EC(50)s and EC(90)s were reduced three- and eightfold, respectively. Kinase Assay: Cell Assay: |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Nitazoxanide is partially effective at reducing the parasite burden in a gnotobiotic piglet diarrhea model when given orally for 11 days at 250 mg/kg/day but not at 125 mg/kg/day. Nitazoxanide induces a drug-related diarrhea in piglets that might have influenced its therapeutic efficacy. | |
| Animal model | Sprague Dawley rats | |
| Dosages | 10 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Tizoxanide (10 mg/kg; i.v.) |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.7700 mL | 18.8501 mL | 37.7003 mL | 75.4006 mL |
| 5mM | 0.7540 mL | 3.7700 mL | 7.5401 mL | 15.0801 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3770 mL | 1.8850 mL | 3.7700 mL | 7.5401 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1885 mL | 0.9425 mL | 1.8850 mL | 3.7700 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.