This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5mg | $135 | 3-6 Days |
| 10mg | $235 | 3-6 Days |
| 25mg | $409 | 3-6 Days |
| 50mg | $610 | 3-6 Days |
| 100mg | $920 | 3-6 Days |
| 250mg | $1600 | 3-6 Days |
Cat #: V3866 CAS #: 1207456-00-5 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Talazoparib racemic (formerly known as BMN 673 and MDV 3800), the racemic mixture of talazoparib, is a potent PARP1/2 [poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase] inhibitor with favorable pharmacokinetic properties.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 380.35 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H14F2N6O |
| CAS No. | 1207456-00-5 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 38 mg/mL (99.9 mM) |
| Water: <1 mg/mL | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
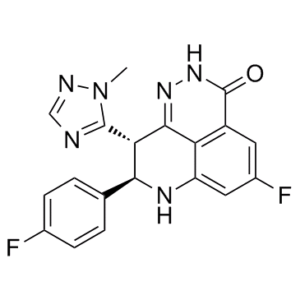
| Solubility In Vivo | O=C1NN=C2C3=C1C=C(F)C=C3N[C@H](C4=CC=C(F)C=C4)[C@H]2C5=NC=NN5C |
| Synonyms | Talazoparib (8R,9S); (8R,9S)-LT-673; BMN 673 racemic; BMN673; BMN-673; LT673; LT 673; LT-673; MDV-3800; MDV 3800; MDV3800; trade name: Talzenna |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: BMN-673 selectively binds to PARP and prevents PARP-mediated DNA repair of single strand DNA breaks via the base-excision repair pathway. This enhances the accumulation of DNA strand breaks, promotes genomic instability and eventually leads to apoptosis. BMN 673 selectively kills cancer cells with BRCA-1 or BRCA-2 mutations. BMN 673 demonstrates single-agent cytotoxicityin BRCA-1 mutant (MX-1, IC50 = 0.3 nM) and BRCA-2 mutant cells (Capan-1, IC50 = 5 nM). In contrast, in MRC-5 normal human fibroblastand other tumor cell lines with wild-type BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 genes, IC50 of BMN 673 ranges between 90 nM and 1.9 μM. In cultured human cancer cells, BMN 673 also significantly enhances the cytotoxic efficacy of both Temozolomide and SN-38. Off-target molecular screening did not identify significant non-specific activity for this class of PARP inhibitors. Kinase Assay: For PARP inhibitor Ki determination, enzyme assays were conducted in 96-well FlashPlate with 0.5 U PARP1 enzyme , 0.25x activated DNA, 0.2 mCi [3H] NAD, and 5 mmol/L cold NAD(Sigma) in a final volume of 50 mL reaction buffer containing 10% glycerol (v/v), 25 mmol/L HEPES, 12.5 mmol/L MgCl2, 50 mmol/L KCl, 1 mmol/L dithiothreitol (DTT), and 0.01% NP-40 (v/v), pH 7.6. Reactions were initiated by adding NAD to the PARP reaction mixture with or without inhibitors and incubated for 1 minute at room temperature. Fifty microliter of ice-cold 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was then added to each well to stop the reaction. The plate was sealed and shaken for a further 120 minutes at room temperature, followed by centrifugation. Radioactive signal bound to the FlashPlate was determined using Top-Count. PARP1 Km was determined using Michaelis–Menten equation from various substrate concentrations (1–100 mmol/L NAD). Compound Ki was calculated from enzyme inhibition curve according to the formula: Ki ¼ IC50/[1þ (substrate)/Km]. Km for PARP2 enzyme and compound Ki were determined with the same assay protocol except 30 ng PARP2, 0.25x activated DNA, 0.2 mCi [3H] NAD, and 20 mmol/L cold NAD were used in the reaction for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cell Assay: BMN 673 exhibits a potent inhibitory effect on a panel of 11 SCLC cell lines (IC50=1.7 to 15 nmol/L), which are all within clinically achievable ranges. In addition, sensitivity to BMN673 correlates to DNA repair protein expression and PI3K pathway activity. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In rat pharmacokinetic studies, BMN 673 displays >50% oralbioavailability and pharmacokinetic properties that enable singledaily dosing. In MX-1 xenograft tumor model studies, daily oral dosingof BMN 673 significantly enhances the antitumor effects ofcytotoxic therapies in a dose-dependent manner. | |
| Animal model | Nude mice bearing established subcutaneous MX-1 tumor xenografts. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.6292 mL | 13.1458 mL | 26.2916 mL | 52.5831 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5258 mL | 2.6292 mL | 5.2583 mL | 10.5166 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2629 mL | 1.3146 mL | 2.6292 mL | 5.2583 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1315 mL | 0.6573 mL | 1.3146 mL | 2.6292 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































