Stenoparib (E7449)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1350 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $2080 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $4200 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3300 CAS #: 1140964-99-3 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Stenoparib (formerly E-7449; 2X-121) is a novel, potent and orally bioavailable dual inhibitor of PARP1/2 [nuclear enzymes poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase] and tankyrases (TNKS1/2) with anticancer activity.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 317.34 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H15N5O |
| CAS No. | 1140964-99-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: ≥ 5mg/mLr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
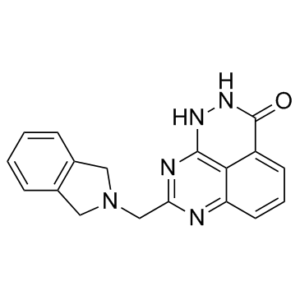
| SMILES Code | O=C1NN=C(N2)C3=C(C=CC=C31)N=C2CN(C4)CC5=C4C=CC=C5 |
| Synonyms | Stenoparib; E7449; 2X-121; E 7449; 2X 121; E-7449; 2X121 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Stenoparib is a potent PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor and also inhibits TNKS1 and TNKS2, with IC50s of 2.0, 1.0, ∼50 and ∼50 nM for PARP1, PARP2, TNKS1 and TNKS2, respectively, using 32P-NAD+ as substrate. Stenoparib shows no obvious inhibiotry effects on PARP3 or PARPs 6-16. Stenoparib traps PARP1 onto damaged DNA, and affects DNA repair pathways beyond homologous recombination (HR). Stenoparib most potnetly suppresses cells deficient in components of the HR pathway (BRCA1 and 2, CtIP, Rad54). Stenoparib (10 μM) inhibits Wnt signaling in SW480 cells |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Stenoparib moderately inhibits the growth of tumors at 100 mg/kg, and significantly ehhances the inhibition via 10, 30 and 100 mg/kg oral dosing in combination with temozolomide (TMZ) in the mouse melanoma B16-F10 isograft model. Stenoparib (30 or 100 mg/kg, p.o.) inhibits PARP, shows anti-tumor activity, and is well-tolerated without any obvious body weight loss or deaths in a BRCA mutant xenograft model. Stenoparib (30, 100 or 300 mg/kg, p.o.) suppresses re-growth of hair in a dose dependent manner, and blocks Wnt signaling in C57BL/6 mice. Stenoparib (100 mg/kg, p.o.) combined with MEK inhibitor exhibits antitumor activity in a Wnt1 subcutaneous model (mammary tumors initially isolated from Wnt1 (int-1) transgenic mice) |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.1512 mL | 15.7560 mL | 31.5119 mL | 63.0239 mL |
| 5mM | 0.6302 mL | 3.1512 mL | 6.3024 mL | 12.6048 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3151 mL | 1.5756 mL | 3.1512 mL | 6.3024 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1576 mL | 0.7878 mL | 1.5756 mL | 3.1512 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































