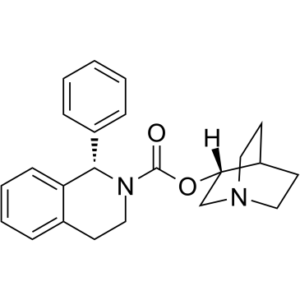
Solifenacin (YM905)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 2g | $250 | Check With Us |
| 10g | $650 | Check With Us |
| 20g | $975 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3721 CAS #: 242478-37-1 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Solifenacin (YM-905; Vesikur; Vesicare) is a novel and potent muscarinic receptor antagonist that has been approved for the treatment of overactive bladder.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 362.46 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H26N2O2 |
| CAS No. | 242478-37-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 72 mg/mL (198.6 mM)r |
| Water: <1mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol:<1mg/mL | |
| Synonyms | YM905; YM 905; YM-905; Solifenacin succinate; Trade name: Vesikur; Vesicare. |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Solifenacin is a novel muscarinic receptor antagonist with pKis of 7.6±0.056, 6.9±0.034 and 8.0±0.021 for M1, M2 and M3 receptors, respectively. In murine submandibular gland cells, the antagonistic effects of 100 nM Solifenacin and oxybutynin on Ca2+ mobilization evoked by varying doses of carbachol (CCh) are examined. Solifenacin does not shift the CCh dose-activation curve in a parallel manner whereas oxybutynin shows insurmountable antagonism. The pKb values are obtained as 7.4±0.17 for Solifenacin and 8.8±0.21 for oxybutynin |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Solifenacin reduces bladder responses by 40% at a dose of 210 nmol/kg (0.1 mg/kg) and abolishes them at 2100 nmol/kg (1 mg/kg). In contrast, its inhibitory effects on salivary and cardiac responses are only slight at 630 nmol/kg (0.3 mg/kg), and reach 66% and 49%, respectively, at 2100 nmol/kg (1 mg/kg). At doses of 63 and 210 nmol/kg (0.03 and 0.1 mg/kg), Solifenacin slightly increases saliva secretion |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.7589 mL | 13.7946 mL | 27.5893 mL | 55.1785 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5518 mL | 2.7589 mL | 5.5179 mL | 11.0357 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3795 mL | 2.7589 mL | 5.5179 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1379 mL | 0.6897 mL | 1.3795 mL | 2.7589 mL |
| Quality Control Documentation |
|
|---|
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































