This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
Cat #: V5204 CAS #: 148554-65-8 Purity ≥ 98%
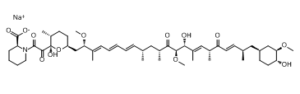
Description: Seco Rapamycin sodium (Secorapamycin A monosodium), the sodium salt of the ring-opened product of Rapamycin, is reported not to affect the mTOR function. Rapamycin (also known as Sirolimus), a natural macrocyclic lactone isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces hygroscopicus, is a specific and potent mTOR inhibitor with IC50 of ~0.1 nM in HEK293 cells. Rapamycin was used as a kind of original antifungal antibiotic, but since it also demonstrated immunosuppressant properties, it is being used in the prevention of transplant rejection because of its immunosuppressive effect. It also exhibits activity against several transplantable tumors and slightly activity to inactive against leukemias. The immunosuppressive effect of Rapamycin is exerted by inhibiting the activation and proliferation of T cells. Rapamycin binds to FK-binding protein 12 (FKBP12) and forms the rapamycin-FKBP12 complex, which regulates an enzyme that plays an important role in the progression of the cell cycle.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 936.15 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₅₁H₇₈NNaO₁₃ |
| CAS No. | 148554-65-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >40 mg/mL |
| Water: <1 mg/mL | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In Vitro Assay: Disposition of Seco Rapamycin in Human Tissue Homogenates and Caco-2 Cell Monolayers. To determine whether Seco Rapamycin (D2) can be metabolized to dihydro Sirolimus (M2), 20 μM Seco Rapamycin is incubated with human liver, jejunal mucosal, and Caco-2 homogenates. All of these homogenates produced M2 in an NADPH-dependent manner. Ketoconazole, at a high concentration (100 μM), has no effect on the formation of M2 in any of the homogenates examined. To determine whether Seco Rapamycin can be metabolized to M2 in intact cells, 20 μM Seco Rapamycin is added to Caco-2 cell monolayers. When applied to the apical compartment, little Seco Rapamycin is detected in the basolateral compartment and in the cellular fraction after 4 h. In addition, little M2 is detected. LY335979 has little effect on the distribution of Seco Rapamycin after an apical dose, although M2 became detectable in the apical compartment. In contrast, when Seco Rapamycin is applied to the basolateral compartment, both Seco Rapamycin and M2 are readily detected in the apical compartment; LY335679 decreases the flux of Seco Rapamycin to the apical compartment and increases the amount of M2 in both apical and basolateral compartments Cell Assay: To determine whether the Sirolimus metabolite M2 is formed from the degradation product Seco Rapamycin, duplicate Caco-2 cell cultures are dosed apically or basolaterally with 20 μM Seco Rapamycin and incubated for 4 h. To determine whether Seco Rapamycin is a substrate for P-gp, duplicate cultures are incubated with 0.5 μM LY335979 in the same manner for Sirolimus. For comparison, a parallel set of cultures is incubated similarly with 20 μM Sirolimus, but dosed apically only. M2 formation is also examined in human jejunal mucosal and liver homogenates and Caco-2 homogenates by incubating each preparation, in duplicate, with 20 μM Seco Rapamycin in the same manner for Sirolimus. For comparison, a parallel set of incubations containing 20 μM Sirolimus is also performed. To determine whether a high dose of Ketoconazole (100 μM) inhibits the formation of M2, parallel experiments with Caco-2 cells and the various homogenates are performed in a similar manner, only Ketoconazole (dissolved as a 100-fold concentration solution in ethanol) is included in the incubation medium/mixtures |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.0682 mL | 5.3410 mL | 10.6820 mL | 21.3641 mL |
| 5mM | 0.2136 mL | 1.0682 mL | 2.1364 mL | 4.2728 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1068 mL | 0.5341 mL | 1.0682 mL | 2.1364 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0534 mL | 0.2671 mL | 0.5341 mL | 1.0682 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































