Scopolamine HBr (Hyoscine)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 1g | $480 | Check With Us |
| 2g | $750 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $1130 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0034 CAS #: 114-49-8 Purity ≥ 98%
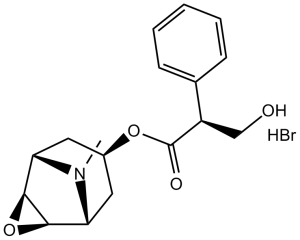
Description: Scopolamine HBr, also known as Hyoscine, is the hydrobromide salt of scopolamine which is a competitive and non-selective antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor with an IC50 of 55.3 nM.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 384.26 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H21NO4.HBr |
| CAS No. | 114-49-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formrrrr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 76 mg/mL (197.8 mM)rrrr |
| Water: 76 mg/mL (197.8 mM)rrrr | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| Solubility In Vivo | N/A |
| Synonyms | Scopolamine HBr, (-)-Scopolamine hydrobromide, Scoburen; Hyoscine |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Application of Scopolamine to oocytes expressing 5-HT3 receptors does not elicit a response when applied alone, but causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of the response during a co-application of 2 μM 5-HT. The pIC50 value for Scopolamine is 5.68±0.05 (IC50=2.09 μM, n=6) with a Hill Slope of 1.06 ± 0.05. This gave a Kb of 3.23 μM. The same concentration-dependent effect is also seen when Scopolamine is applied during the 5-HT application. To further test for a competitive binding at the 5-HT3 receptor, the competition of unlabelled Scopolamine is measured with [3H]granisetron, an established high-affinity competitive antagonist at these receptors. Scopolamine displays concentration-dependent competition with 0.6 nM [3H]granisetron (~Kd), yielding an average pKi of 5.17±0.24 (Ki=6.76 μM, n=3) |
|---|
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.6024 mL | 13.0120 mL | 26.0240 mL | 52.0481 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5205 mL | 2.6024 mL | 5.2048 mL | 10.4096 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2602 mL | 1.3012 mL | 2.6024 mL | 5.2048 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1301 mL | 0.6506 mL | 1.3012 mL | 2.6024 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































