Rucaparib phosphate (AG014699; PF01367338)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $790 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1350 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $4010 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0302 CAS #: 459868-92-9 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Rucaparib (formerly AG-014699 or PF-01367338; trade name: Rubraca) is a potent, tricyclic indole based, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of PARP (poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase) with potential anticancer activity.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 421.36 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H18FN3O.H3PO4 |
| CAS No. | 459868-92-9 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 84 mg/mL (199.4 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| Solubility In Vivo | 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30 mg/mL |
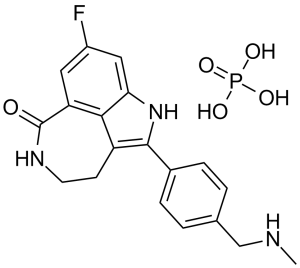
| Synonyms | AG014699; PF-01367338; AG 014699; PF 01367338; AG-014699,PF01367338; AG-14447; AG 14447; AG14447; Trade name: Rubraca; Rucaparib Chemical Name: 8-fluoro-2-(4-((methylamino)methyl)phenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6(3H)-one phosphate InChi Key: FCCGJTKEKXUBFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N InChi Code: InChI=1S/C19H18FN3O.H3O4P/c1-21-10-11-2-4-12(5-3-11)18-14-6-7-22-19(24)15-8-13(20)9-16(23-18)17(14)15;1-5(2,3)4/h2-5,8-9,21,23H,6-7,10H2,1H3,(H,22,24);(H3,1,2,3,4) SMILES Code: O=C1NCCC2=C(C3=CC=C(CNC)C=C3)NC4=C2C1=CC(F)=C4.O=P(O)(O)O |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Rucaparib (AG014699) phosphate is a possible N-demethylation metabolite of AG14644 |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Rucaparib (AG014699) phosphate and AG14584 significantly increase Temozolomide toxicity. Rucaparib (1 mg/kg) phosphate significantly increases Temozolomide-induced body weight loss. Rucaparib (0.1 mg/kg) phosphate results in a 50% increase in the temozolomide-induced tumor growth delay | |
| Animal model | Female athymic nude mice, implanted SW620 colorectal tumor cells (1 × 107 cells per animal) s.c. | |
| Dosages | 0.1 mg/kg in combination with Temozolomide (p.o., 200 mg/kg), 0.05, 0.15, and 0.5 mg/kg in combination with Temozolomide (p.o., 68 mg/kg) or 10 mg/kg | |
| Administration | IP, single dose for 0.1 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, five daily doses for 0-0.5 mg/kg |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.3733 mL | 11.8663 mL | 23.7327 mL | 47.4654 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4747 mL | 2.3733 mL | 4.7465 mL | 9.4931 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2373 mL | 1.1866 mL | 2.3733 mL | 4.7465 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1187 mL | 0.5933 mL | 1.1866 mL | 2.3733 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































