This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $290 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $470 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $1175 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2329 CAS #: 61379-65-5 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Rifapentine (formerly also known as MDL473; Priftin; DL 473, Cyclopentylrifampicin) is a potent antibiotic/antimicrobial of the rifamycin class, used to treat tuberculosis. It inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity. Rifapentine inhibits the function of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in strains of M. tuberculosis, while inducing no effect on mammalian cells. Both Rifapentine and its active metabolite, 25-desacetylrifapentine, localize within monocyte-derived macrophages, thus allowing for intracellular inhibition of M. tuberculosis at a greater kill rate as compared with that of the parent or metabolite alone. Rifapentine is deacetylated in the liver and induces cytochrome P450 much less than rifampin.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 877.03 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C47H64N4O12 |
| CAS No. | 61379-65-5 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (114.0 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: 17 mg/mL (19.4 mM) | |
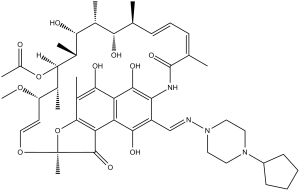
| SMILES Code | CO[C@H]1/C=C/O[C@]2(Oc(c(C)c3O)c(C2=O)c4c3c(O)c(NC(/C(C)=C\C=C\[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]1C)OC(C)=O)C)O)C)O)C)=O)c(/C=N/N5CCN(C6CCCC6)CC5)c4O)C |
| Synonyms | MDL473; MDL 473; MDL-473; DL 473; DL-473; DL473; R 773; R-773; R773; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: The activities of rifampin and rifapentine against Mycobacterium tuberculosis residing in human monocytederived macrophages were determined. The MIC and MBC of rifapentine for intracellular bacteria were two- to four-fold lower than those of rifampin. For extracellular bacteria, this difference was less noticeable. Cell Assay: Rifapentine inhibits the function of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in strains of M. tuberculosis, while inducing no effect on mammalian cells. Both Rifapentine and its active metabolite, 25-desacetylrifapentine, localize within monocyte-derived macrophages, thus allowing for intracellular inhibition of M. tuberculosis at a greater kill rate as compared with that of the parent or metabolite alone. Rifapentine is deacetylated in the liver and induces cytochrome P450 much less than rifampin. Rifapentine has shown higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities (MICs and MBCs) than RMP, especially against intracellular bacteria growing in human monocyte-derived macrophages. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Rifapentine inhibits bacterial RNA synthesis by binding to the β-subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in susceptible species. Rifapentine is generally more active than rifampicin against sensitive strains of M. tuberculosis. Rifapentine significantly increases the rate of antipyrine and pentobarbital metabolism in vivo. Rifapentine also increases liver weight, the content of liver microsomal protein and cytochrome P-450, the activity of NADPH-cytochrome C reductase and NADPH oxidase. Rifapentine combined with isoniazid (INH) and pyrazinamide (PZA) administered daily results in an apparent clearance of M.tuberculosis organisms in the lungs and spleens of infected mice after 10 weeks of treatment | |
| Animal model | Mice |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.1402 mL | 5.7011 mL | 11.4021 mL | 22.8042 mL |
| 5mM | 0.2280 mL | 1.1402 mL | 2.2804 mL | 4.5608 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1140 mL | 0.5701 mL | 1.1402 mL | 2.2804 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0570 mL | 0.2851 mL | 0.5701 mL | 1.1402 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































