This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $450 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $750 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $2025 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3926 CAS #: 1374639-79-8 Purity ≥ 98%
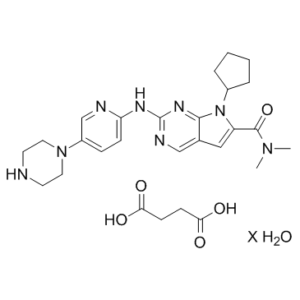
Description: Ribociclib succinate hydrate (LEE011; LEE-011; NVP-LEE-011; NVP-LEE011; Kisqali), the succinate salt and hydrated form of Ribociclib, is a potent inhibitor of CDK4/6 (cyclin-dependent kinase) (IC50s = 10 nM and 39 nM) approved in March 2017 by FDA for the treatment of breast cancer.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 570.64 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₂₇H₃₈N₈O₆ |
| CAS No. | 1374639-79-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: ≥ 19 mg/mLr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Synonyms | LEE011 succinate hydrate; LEE-011 succinate; LEE 011 succinate; trade name: Kisqali |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Treating a panel of 17 neuroblastoma cell lines with Ribociclib (LEE011) across a four-log dose range (10 to 10,000 nM). Treatment with Ribociclib significantly inhibits substrate adherent growth relative to the control in 12 of the 17 neuroblastoma cell lines examined (mean IC50=306±68 nM, considering sensitive lines only, where sensitivity is defined as an IC50 of less than 1 μM. Ribociclib treatment of two neuroblastoma cell lines (BE2C and IMR5) with demonstrated sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibition results in a dose-dependent accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. This G0/G1 arrest becomes significant at Ribociclib concentrations of 100 nM (p=0.007) and 250 nM (p=0.01), respectively. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | CB17 immunodeficient mice bearing BE2C, NB-1643 (MYCN amplified, sensitive in vitro), or EBC1 (non-amplified, resistant in vitro) xenografts are treated once daily for 21 days with Ribociclib (LEE011; 200 mg/kg) or with a vehicle control. This dosing strategy is well tolerated, as no weight loss or other signs of toxicity are observed in any of the xenograft models. Tumor growth is significantly delayed throughout the 21 days of treatment in mice harboring the BE2C or 1643 xenografts (both, p<0.0001), although growth resumed post-treatment |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.7524 mL | 8.7621 mL | 17.5242 mL | 35.0484 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3505 mL | 1.7524 mL | 3.5048 mL | 7.0097 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1752 mL | 0.8762 mL | 1.7524 mL | 3.5048 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0876 mL | 0.4381 mL | 0.8762 mL | 1.7524 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































