This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $700 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1150 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $2900 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2176 CAS #: 224452-66-8 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Retapamulin (also known as SB-275833) is a novel and potent topical antibiotic of the pleuromutilin class approved by the FDA for treatment of impetigo in children. It binds to both E. coli and S. aureus ribosomes with similar potencies with Kd of 3 nM. It has low potential for the development of antibacterial resistance and a high degree of potency against poly drug resistant Gram-positive bacteria found in skin infections including Staphylococcus aureus strains. The drug is safe owing to low systemic absorption and has only minimal side-effect of local irritation at the site of application.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 517.76 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H47NO4S |
| CAS No. | 224452-66-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO:104 mg/mL (200.86 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol:104 mg/mL (200.86 mM) | |
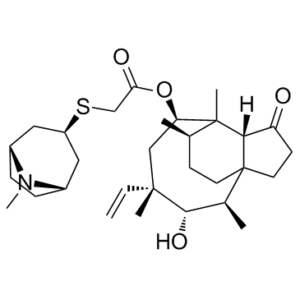
| SMILES Code | O=C(O[C@@H]1C[C@](C=C)(C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@]2(CCC3=O)[C@]3([H])[C@]1(C)[C@H](C)CC2)CS[C@@H]4C[C@@](N5C)([H])CC[C@@]5([H])C4 |
| Synonyms | SB-275833; SB 275833; SB275833; Retapamulin, trade names Altabax and Altargo. |
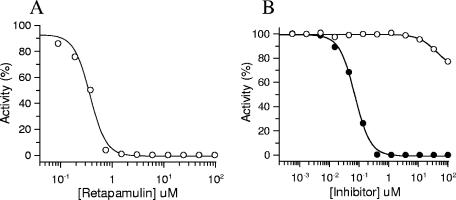
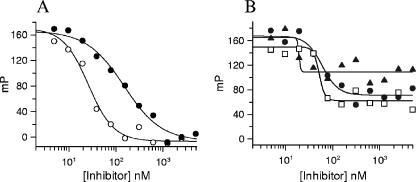
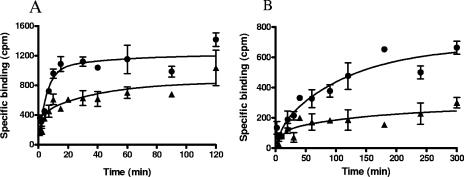
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity:Retapamulin is a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis with an IC50 of 0.33 μM in lysates prepared from erythromycin-susceptible E. coli cells. Retapamulin (100 μM) is ineffective in inhibiting eukaryotic translation when tested in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate system with the cellular components necessary for mammalian protein synthesis. Retapamulin binds to Erys ribosomes and fully displaces the labeled ligand with an IC50 of 26.1 nM. Retapamulin partially inhibits the ability of charged, N-blocked tRNA to bind to the P-site of E. coli ribosomes, with an IC50 of 17.4 nM (maximum inhibition of 80%). Retapamulin inhibits Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes with MIC90 of 0.12 μg/mL and ≤0.03 μg/mL, respectively. Retapamulin inhibits S. aureus subset with MIC50/90 values of 0.06/0.12 μg/mL. Retapamulin shows excellent activity against these isolates, with only two requiring a MIC of 0.06 μg/mL. Retapamulin is very active against the S. pyogenes isolates tested with MIC90 of 0.016 μg/mL, and based on MIC90s, is 32- and >1,024-fold more active than mupirocin and fusidic acid, respectively. Retapamulin binds to a unique site on the bacterial ribosome, and by virtue of its novel mode of action. Retapamulin (<2 mg/L) inhibits 37/52 (71%) strains of the B. fragilis group and 85/87 (98%) of the other Gram-negative bacilli. Retapamulin is more active than clindamycin, metronidazole and ceftriaxone against Propionibacterium acnes and anaerobic Gram-positive cocci. Retapamulin inhibits total viable cells (TVC), Protein synthesis and 50S subunit synthesis in both wild-type (wt) Staphylococcus aureus strain RN1786 with IC50 of 12 ng/mL, 5 ng/mL and 27 ng/mL, respectively. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.9314 mL | 9.6570 mL | 19.3140 mL | 38.6279 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3863 mL | 1.9314 mL | 3.8628 mL | 7.7256 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1931 mL | 0.9657 mL | 1.9314 mL | 3.8628 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0966 mL | 0.4828 mL | 0.9657 mL | 1.9314 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.