This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1500 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $2250 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $3375 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0676 CAS #: 260415-63-2 Purity ≥ 98%
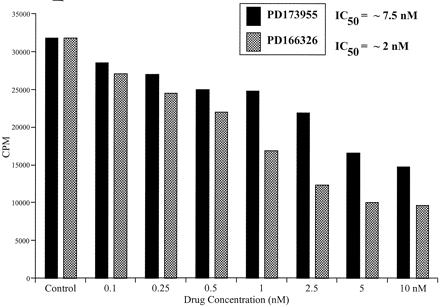
Description: PD173955 (PD-173955), a src-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is a novel and potent Bcr-Abl inhibitor with potential anticancer activity. It inhibits Bcr-Abl with an IC50 of 1-2 nM, it also inhibits Src activity with IC50 of 22 nM.
References: [1]. Moasser MM, et al. Inhibition of Src kinases by a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor causes mitotic arrest. Cancer Res. 1999 Dec 15;59(24):6145-52.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 443.35 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H16Cl2N4OS |
| CAS No. | 260415-63-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formrr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 15 mg/mL (33.8 mM)rr |
| Water:<1 mg/mLrr | |
| Ethanol:<1 mg/mL | |
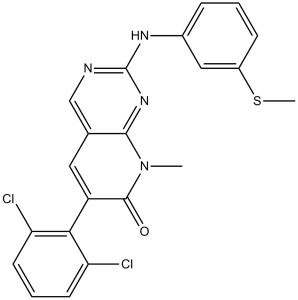
| SMILES Code | O=C1C(C2=C(Cl)C=CC=C2Cl)=CC3=CN=C(NC4=CC=CC(SC)=C4)N=C3N1C |
| Synonyms | PD 173955; PD173955; PD-173955 |
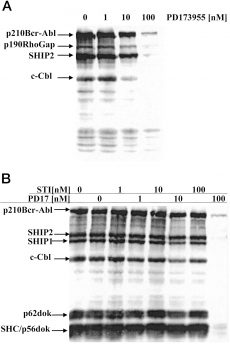
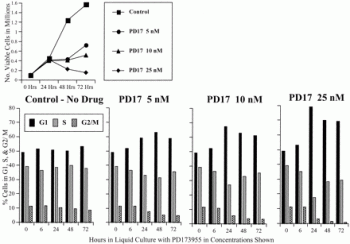
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: PD173955 potently inhibits Bcr-Abl-dependent cell growth with IC50 of 2-35 nM in Bcr-Abl-positive cell lines, about 100- to 200-fold more sensitive than in Bcr-Abl-negative cell lines. PD173955 also inhibits kit ligand-dependent proliferation of M07e cells with IC50 of 40 nM, by inhibition of kit ligand-dependent c-kit autophosphorylation. In addition, PD173955, as a Src inhibitor, potently inhibits mitotic progression during early mitosis in cells of all types and induces varying degrees of apoptotic cell death. Kinase Assay: Bcr-Abl complexed to SHIP2 is immunoprecipitated from cell lysates of K562 cells maintained in log-phase culture conditions. Complexes are collected on protein A-Sepharose, and complexes are washed three times in lysis buffer and then washed twice in abl kinase buffer [50 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 2 mM p-nitrophenylphosphate, and 2 μM ATP; New England Biolabs Buffer and protocol]. Kinase assays are performed with 10 μM [γ-32P]ATP/sample for 15–60 min at 30°C in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of drug. The reaction is stopped by the addition of SDS-PAGE sample buffer and heated at 100°C for 10 min. Proteins are separated on 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, gels are dried under vacuum, and phosphorylation is visualized by autoradiography on X-ray film. Cell Assay: Cell growth is determined by two methods. For the [3H]thymidine assay, cells (104 cells/well, Bcr-Abl-positive cell lines (R10(+), R10(−), K562, and RWLeu4); Bcr-Abl-negative cell lines (HL-60, SK-N-ER, SK-N-MC, U138MG, and HS-16)) are cultured in 96-well, round-bottomed plates with diluted DMSO (control) or with varying concentrations of a specific compound that is resuspended in DMSO for 48 h at 37°C. [3H]Thymidine is added at a concentration of 1 μCi/well, and cells are incubated for an additional 18 h. Cells were harvested with the Unifilter system, scintillation fluid (25 μl/well) is added to each well, and [3H]thymidine incorporation is determined on a Packard Scintillation Counter. Data points for all assays are obtained in triplicate, and background incorporation from cell-free wells is determined and subtracted from all data points. For cell viability, control and drug-treated harvested cells are counted on a hemocytometer using the trypan blue dye exclusion method. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.2556 mL | 11.2778 mL | 22.5555 mL | 45.1111 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4511 mL | 2.2556 mL | 4.5111 mL | 9.0222 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2256 mL | 1.1278 mL | 2.2556 mL | 4.5111 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1128 mL | 0.5639 mL | 1.1278 mL | 2.2556 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.