This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $1350 | Check With Us |
| 250mg | $2300 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $3450 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3869 CAS #: 1075240-43-5 Purity ≥ 98%
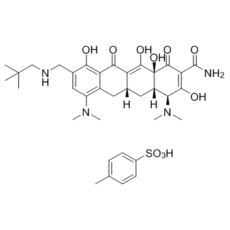
Description: Omadacycline tosylate (formerly PTK0796; trade name: Nuzyra), the tosylate salt of omadacycline, is a tetracycline antibiotic being developed as an oral and intravenous (IV) formulation to treat community-acquired bacterial infections such as acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP), and urinary tract infections (UTI). In Oct 2018, Omadacycline was approved by FDA to treat community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 728.86 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H48N4O10S |
| CAS No. | 1075240-43-5 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Synonyms | PTK 0796 tosylate; PTK-0796; PTK0796; Amadacyclin tosylate |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Omadacycline is a novel, aminomethyl tetracycline antibiotic being developed for oral and intravenous (IV) administration to treat community-acquired bacterial infections such as acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI), community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP), and urinary tract infections (UTI). In vitro, omadacycline has activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobes, anaerobes, and atypical pathogens including Legionella and Chlamydia spp. Omadacycline offers once daily oral and IV dosing and a clinical tolerability and safety profile that compares favorably with contemporary antibiotics used across serious community-acquired infections where resistance has rendered many less effective. In studies in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections, including those with MRSA infections, omadacycline exhibited an efficacy and tolerability profile that was comparable to linezolid. Ongoing and planned clinical studies are evaluating omadacycline as monotherapy for treating serious community-acquired bacterial infections including Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections (ABSSSI) and Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP). This review provides an overview of the discovery, microbiology, nonclinical data, and available clinical safety and efficacy data for omadacycline, with reference to other contemporary tetracycline-derived antibiotics. Cell Assay: The omadacycline MIC90s for MRSA, VRE, and beta-hemolytic streptococci are 1.0 μg/mL, 0.25 μg/mL, and 0.5 μg/mL, respectively, and the omadacycline MIC90s for PRSP and H. influenzae are 0.25 μg/ml and 2.0 μg/mL, respectively. Omadacycline is active against organisms demonstrating the two major mechanisms of resistance, ribosomal protection and active tetracycline efflux[1]. Omadacycline inhibits protein synthesis while having no significant effect on RNA, DNA and peptidoglycan synthesis. Further, omadacycline binds to the tetracycline binding site on the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome with enhanced binding similar to tigecycline based on additional molecular interactions. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In vivo efficacy of omadacycline is demonstrated using an intraperitoneal infection model in mice. A single intravenous dose of omadacycline exhibits efficacy against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus, including tet (M) and tet (K) efflux-containing strains and MRSA strains. The 50% effective doses (ED50s) for Streptococcus pneumoniae obtained ranged from 0.45 mg/kg to 3.39 mg/kg, the ED50s for Staphylococcus aureus obtained ranges from 0.30 mg/kg to 1.74 mg/kg, and the ED50 for Escherichia coli is 2.02 mg/kg. | |
| Animal model | Mice | |
| Dosages | 0.45 mg/kg to 3.39 mg/kg | |
| Administration | i.p. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.3720 mL | 6.8600 mL | 13.7201 mL | 27.4401 mL |
| 5mM | 0.2744 mL | 1.3720 mL | 2.7440 mL | 5.4880 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1372 mL | 0.6860 mL | 1.3720 mL | 2.7440 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0686 mL | 0.3430 mL | 0.6860 mL | 1.3720 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































