NS 1738 (NSC 213859)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1125 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1800 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2700 | Check With Us |
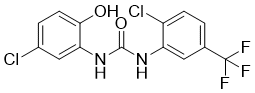
Cat #: V5093 CAS #: 501684-93-1 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: NS 1738 (also known as NSC 213859) is a novel and potent positive allosteric modulator of the α7 nAChR, with respect to positive modulation of nicotinic alpha7 receptor (α7 nAChR) with EC50 of 3.4 μM in oocyte experiments.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 365.13 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H9Cl2F3N2O2 |
| CAS No. | 501684-93-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent |
| Protocol | In Vitro | NS 1738 acts by increasing the peak amplitude of acetylcholine (ACh)-evoked currents at all concentrations; thus, it increased the maximal efficacy of ACh. Plotting peak current amplitude against the logarithm of the NS 1738 concentration used for preincubation reveals a sigmoidal concentration-response relationship that is well fit by the Hill equation (EC50=3.4 μM). Under similar experimental conditions, NS 1738 shows comparable efficacy and potency at the rat α7 nAChR (EC50=3.9 μM) |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | To estimate the ability of NS 1738 to permeate the blood-brain barrier, rats are administered 10 mg/kg NS 1738 intraperitoneally. Peak brain concentrations are measured approximately 30 min after injection, and they amount to ~80 ng/mL (~200 nM) at this dose. The ratio between the amount of compound entering the brain and that in plasma is AUCbrain/AUCplasma=0.50. The half-life in plasma is estimated to 42 min. Incubation of NS1738 with isolated liver microsomes in vitro indicates that approximately 60 and 75% of NS 1738 is metabolized via the cytochrome P450 system in mouse and rat, respectively, within 1 h. Adult rats administered NS 1738 at 10 and 30 mg/kg i.p. immediately following the initial exposure to a juvenile rat (T1) display significant decreases in the investigative duration of a subsequent exposure to the same juvenile (T2) 2 h later (T2/T1 ratio of 0.69±0.13 and 0.61±0.07, respectively). |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.7388 mL | 13.6938 mL | 27.3875 mL | 54.7750 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5478 mL | 2.7388 mL | 5.4775 mL | 10.9550 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2739 mL | 1.3694 mL | 2.7388 mL | 5.4775 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1369 mL | 0.6847 mL | 1.3694 mL | 2.7388 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































