This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 1g | $500 | Check With Us |
| 2g | $900 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $1520 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V20396 CAS #: 315-22-0 Purity ≥ 98%
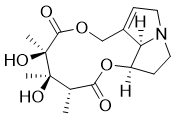
Description: Monocrotaline (NSC-28693; Crotaline) is a naturally occuring pyrrolizidine alkaloid extracted from the seeds of the Crotalaria spectabilis plant, exhibiting dose-dependent cytotoxicity and causing pulmonary artery hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and pathological changes in the pulmonary vasculature.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 325.36 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H23NO6 |
| CAS No. | 315-22-0 |
| SMILES Code | O=C(O[C@]1([H])CCN2[C@]1([H])C(CO3)=CC2)[C@H](C)[C@@](C)(O)[C@@](C)(O)C3=O |
| Synonyms | Monocrotaline; NSC 28693; NSC-28693; NSC28693 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Monocrotaline (MCT) is an 11-membered macrocyclic pyrrolizidine alkaloid (PA) derived from the seeds of the Crotalaria spectabilis plant[1]. Monocrotaline a natural ligand exhibits dose-dependent cytotoxicity with potent antineoplastic activity. The in vitro cytotoxicity of monocrotaline is proved at IC50 24.966 µg/mL and genotoxicity at 2 X IC50 against HepG2 cells[2]. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | MCT causes a pulmonary vascular syndrome in rats characterized by proliferative pulmonary vasculitis, pulmonary hypertension (PH), and cor pulmonale[3]. Among preclinical models of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), monocrotaline animal model offers the advantage of mimic several key aspects of human PAH, including vascular remodeling, proliferation of smooth muscle cells, endothelial dysfunction, upregulation of inflammatory cytokines, and right ventricle failure, requiring a single drug injection[4]. Changes in multiple pathways associated with the development of PH, including activated glycolysis, increased markers of proliferation, disruptions in carnitine homeostasis, increased inflammatory and fibrosis biomarkers, and a reduction in glutathione biosynthesis are observed with the injection of monocrotaline[5]. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.0735 mL | 15.3676 mL | 30.7352 mL | 61.4704 mL |
| 5mM | 0.6147 mL | 3.0735 mL | 6.1470 mL | 12.2941 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3074 mL | 1.5368 mL | 3.0735 mL | 6.1470 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1537 mL | 0.7684 mL | 1.5368 mL | 3.0735 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































