This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1000 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1550 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2325 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0678 CAS #: 778270-11-4 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: GNF-2 (GNF 2; GNF2) is a highly potent, selective and allosteric/non-ATP competitive inhibitor of Bcr-Abl with potential anticancer activity. It shows no activity against Flt3-ITD, Tel-PDGFR, TPR-MET and Tel-JAK1 transformed tumor cells. GNF-2 acts by allosterically binding the myristate-binding site of ABL and inhibits the proliferation of BCR-ABL positive cell and induces cell apoptosis. GNF-2 eliminated transplanted-CML-T315I-mutants in vivo and dose dependently sensitized primary cells from CML T315I patients to GNF-2-induced proliferation inhibition and apoptosis
References: [1]. Adrián FJ, et al. Allosteric inhibitors of Bcr-abl-dependent cell proliferation. Nat Chem Biol. 2006 Feb;2(2):95-10
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 374.32 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H13F3N4O2 |
| CAS No. | 778270-11-4 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 74 mg/mL (197.69 mM)r |
| Water:<1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
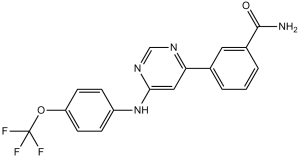
| SMILES Code | O=C(N)C1=CC=CC(C2=NC=NC(NC3=CC=C(OC(F)(F)F)C=C3)=C2)=C1 |
| Synonyms | GNF-2; GNF 2; GNF2; |
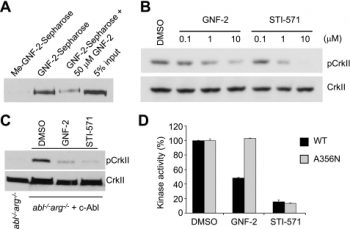
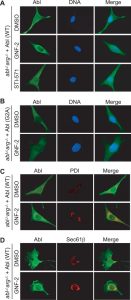
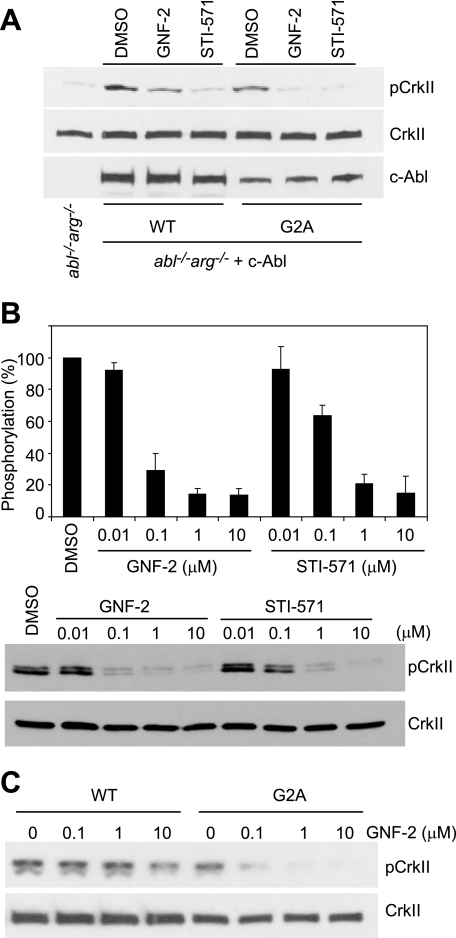
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: GNF-2 causes a dose-dependent growth inhibition of the Bcr-abl–positive cell lines with IC50 values of 273 nM (K562) and 268 nM (SUP-B15). GNF-2 inhibits the growth of Ba/F3.p210E255V and Ba/F3.p185Y253H cells with IC50 values of 268 nM and 194 nM respectively. GNF-2 (1 μM) induces apoptosis of Ba/F3.p210 cells as well as Ba/F3.p210E255V cells. GNF-2 inhibits the cellular tyrosine phosphorylation of Bcr-abl in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 of 267 nM. GNF-2 (1 μM) induces a significant decrease in the levels of phospho-Stat5 in Ba/F3.p210 cells. GNF-2 binds to the myristic binding pocket of Bcr-abl. GNF-2 inhibits the kinase activity of non-myristoylated c-Abl more potently than that of myristoylated c-Abl by binding to the myristate-binding pocket in the C-lobe of the kinase domain. GNF-2 (10 μM) requires BCR and/or the c-Abl SH3 and/or SH2 domains to inhibit BCR-Abl-dependent cell proliferation. GNF-2, but not a methylated GNF-2 analog, binds c-Abl in cellular extracts derived from 3T3 fibroblasts. GNF-2 (10 μM), in a dose-dependent manner, clearly inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of CrkII. GNF-2 inhibits the phosphorylation of CrkII in c-AblG2A-expressing cells with IC50 of 0.051 μM. GNF-2 binds in an extended conformation in the myristate pocket with the CF3-group buried at the same depth as the final two carbons of the myristate ligand. GNF-2 (10 µM) combined with imatinib (1 µM) reduces the number of resistant clones to 1 µM imatinib by at least 90%. GNF-2 inhibits the auto-phosphorylation and proliferation of BafF3 cells expressing p210Bcr–Abl and p210Bcr–Abl mutants. GNF-2 (8 nM) in combination with GNF-5 (20 nM) results in additive effects with respect to inhibition of the Abl64–515 kinase activity. Kinase Assay: Recombinant proteins (100 nM for each construct) or immunoprecipitated proteins are diluted in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 50 mM KCl, 0.1% CHAPS, 30 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 1% glycerol). Aliquots of the diluted proteins are preincubated with either DMSO or compounds for 30 min at room temperature and then added to K-LISA PTK EAY reaction plates. The kinase reaction is initiated by adding 0.1 mM ATP and is allowed to proceed for 30 min at room temperature. The phosphorylation of GST-Abltide is monitored by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging analysis or autoradiography. Cell Assay: Cells (0.3-0.6 × 106 per mL, Ba/F3.p210, Ba/F3.p210E255V and Ba/F3.p185Y253H cells) are plated in duplicate or triplicate in 96-well plates containing increasing GNF-2 concentrations (5 nM–10 μM). After incubation at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2 for 48 hours, the effect of GNF-2 on cell viability is determined by the MTT colorimetric dye reduction method. Inhibition of cell proliferation is calculated as a percentage of growth of DMSO-treated cells, and IC50 values are determined with Microsoft Excel XLfit3. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Combining PDMP and GNF-2 eliminated transplanted-CML-T315I-mutants in vivo and dose dependently sensitized primary cells from CML T315I patients to GNF-2-induced proliferation inhibition and apoptosis |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.6715 mL | 13.3576 mL | 26.7151 mL | 53.4302 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5343 mL | 2.6715 mL | 5.3430 mL | 10.6860 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2672 mL | 1.3358 mL | 2.6715 mL | 5.3430 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1336 mL | 0.6679 mL | 1.3358 mL | 2.6715 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.