This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5g | $545 | Check With Us |
| 10g | $745 | Check With Us |
| 20g | $1110 | Check With Us |
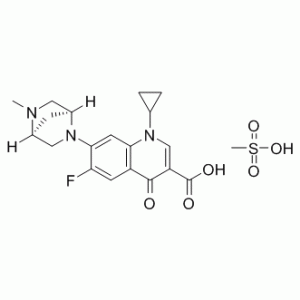
Cat #: V2409 CAS #: 119478-55-6 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Danofloxacin Mesylate (formerly also known as CP-76136-27), the mesylate salt of danofloxacin, is a fluoroquinolone class of antibiotic for veterinary use. It has an MIC90 of 0.28 μM and acts by inhibiting bacterial DNA-gyrase, which is necessary for DNA replication. The minimum inhibitory concentration of danofloxacin against 90% (MIC90) of contemporary European and North American field isolates of Pasteurella haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Haemophilus somnus, the most important bacterial respiratory pathogens of cattle, is 0.125 μg/ml. Danofloxacin shows protective dose (PD50) of 0.38, 0.8, 2.42 mg/kg for P. multocida, E. coli and S. choleraesuis in in vivo mouse protection assay.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 453.48 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H20FN3O3.CH4O3S |
| CAS No. | 119478-55-6 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: <1 mg/mLr |
| Water: 91 mg/mL (200.7 mM)r | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| Solubility In Vivo | Saline: 30 mg/mL |
| SMILES Code | O=C(C1=CN(C2CC2)C3=C(C=C(F)C(N4[C@](C5)([H])CN(C)[C@]5([H])C4)=C3)C1=O)O.CS(=O)(O)=O |
| Synonyms | CP 76,136-27; CP-76,136-27; Danofloxacin monomethanesulfonate |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Danofloxacin is a synthetic antibacterial agent of the fluoroquinolone class, acts principally by the inhibition of bacterial DNA-gyrase, which is necessary for supercoiling of DNA to provide a suitable spatial arrangement of DNA within the bacterial cell. The minimum inhibitory concentration of danofloxacin against 90% (MIC90) of contemporary European and North American field isolates of Pasteurella haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Haemophilus somnus, the most important bacterial respiratory pathogens of cattle, is 0.125 μg/ml. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Danofloxacin shows protective dose (PD50) of 0.38, 0.8, 2.42 mg/kg for P. multocida, E. coli and S. choleraesuis in in vivo mouse protection assay. | |
| Animal model | Mice model |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.2052 mL | 11.0258 mL | 22.0517 mL | 44.1034 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4410 mL | 2.2052 mL | 4.4103 mL | 8.8207 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2205 mL | 1.1026 mL | 2.2052 mL | 4.4103 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1103 mL | 0.5513 mL | 1.1026 mL | 2.2052 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































