This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 10mg | $61 | To Be Confirmed |
| 25mg | $88 | To Be Confirmed |
| 50mg | $130 | To Be Confirmed |
| 100mg | $200 | To Be Confirmed |
| 250mg | $330 | To Be Confirmed |
| 500mg | $480 | To Be Confirmed |
| 1g | $750 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V4273 CAS #: 362-74-3 Purity ≥ 98%
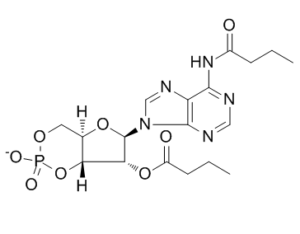
Description: Bucladesine (DC2797; DC-2797; Dibutyryl-cAMP) is a potent and cell-permeable PKA activator and a cAMP analog that mimics the action of endogenous cAMP. It is a cyclic nucleotide derivative (structurally similar to cAMP) and is also a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Dibutyryl-cAMP preferentially activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The products releaes butyrate due to intracellular and extracellular esterase action. Butyrate was shown to have distinct biological effects. The compound is used in a wide variety of research applications because it mimics cAMP and can induce normal physiological responses when added to cells in experimental conditions.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 469.39 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H24N5O8P |
| CAS No. | 362-74-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: N/A |
| Water: N/A | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Solubility In Vivo | 10% DMSO+ddH2O: 30 mg/mL |
| Synonyms | dbcAMP; Dibutyryl-cAMP; DC2797; DC-2797; DC 2797; calcium dibutyryl cAMP; Bucladesine sodium; DbcAMP calcium; Actosin; calcium Dibutyryl cAMP; Cyclic dibutyryl-AMP calcium salt; DT 5621; Actosin; Bucladesina; DBC-AMP |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Bucladesine sodium (also known as Dibutyryl-cAMP) is a cell-permeable PKA activator and a cAMP analog that mimics the action of endogenous cAMP. It is a cyclic nucleotide derivative (structurally similar to cAMP) and is also a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Dibutyryl-cAMP preferentially activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The products releaes butyrate due to intracellular and extracellular esterase action. Butyrate was shown to have distinct biological effects. The compound is used in a wide variety of research applications because it mimics cAMP and can induce normal physiological responses when added to cells in experimental conditions. Kinase Assay: Bucladesine sodium (also known as Dibutyryl-cAMP) is a cell-permeable PKA activator and a cAMP analog that mimics the action of endogenous cAMP. It is a cyclic nucleotide derivative (structurally similar to cAMP) and is also a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Dibutyryl-cAMP preferentially activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase. |
|---|---|---|
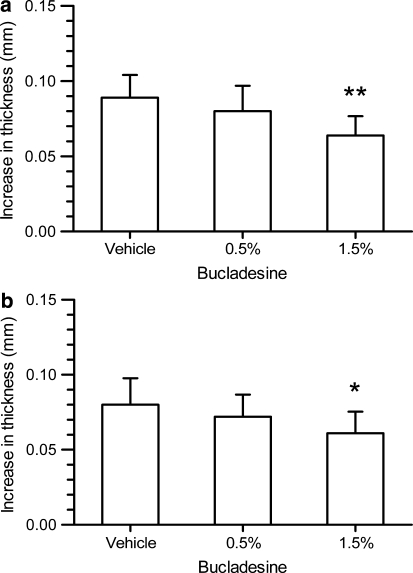
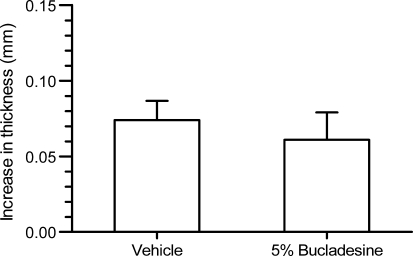
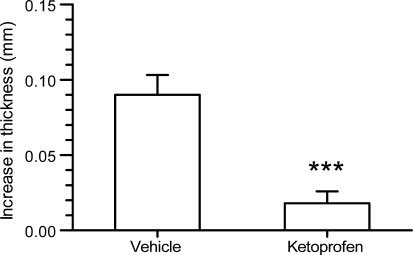
| In Vivo | Experimentally naïve male Albino Swiss mice (Laboratory Animals Breeding, Słaboszów, Poland) weighing 20–30 g were used in all experiments. The animals were housed in polycarbonate cages at a controlled temperature (23–25°C) and humidity (50–60%) with 12 h light/dark cycle (lights on at 6 h). Tap water and food pellets were available ad libitum. All experiments were performed after at least 7 days of acclimatization. The experimental protocols were approved by the Ethical Committee of the Medical University in Lublin (license number 40/2010). To allow for skin penetration of the cream formulations and based on preliminary experiments with ketoprofen cream in this model (data not presented), a pre-treatment time of 3 h was selected. To evaluate the effect of 0.5 or 1.5% bucladesine cream, an amount of 10 ± 1 mg cream each was spread onto the outer surface of both, left and right ears using small spatula. A third group of mice was administered with 2.5% ketoprofen gel. Corresponding vehicle treatment groups were administered either the respective cream base without bucladesine or, as reference for ketoprofen, a cosmetic night cream. To evaluate the effect of repeated administration, four separate groups of mice were dosed twice, i.e., 7 and 3 h before administration of arachidonic acid with the 0.5 and 1.5% cream or corresponding vehicle. Arachidonic acid or actetone were administered 3 h after the second cream administration onto left and right ears, respectively. The ear thickness was measured with a precise spring-loaded caliper (Mitutoyo, type 7309, Kawasaki, Japan) before and 60 min after application of arachidonic acid or vehicle. | |
| Animal model | Naïve male Albino Swiss mice |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.1304 mL | 10.6521 mL | 21.3042 mL | 42.6085 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4261 mL | 2.1304 mL | 4.2608 mL | 8.5217 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2130 mL | 1.0652 mL | 2.1304 mL | 4.2608 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1065 mL | 0.5326 mL | 1.0652 mL | 2.1304 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.