This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $650 | Check With Us |
| 200mg | $975 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1625 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0095 CAS #: 1985606-14-1 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Baloxavir marboxil (BXM or S-033188) is the prodrug of Baloxavir (trade name Xofluza; also known as Baloxavir acid, BXA,or S-033447) which is an approved antiviral drug developed by Roche and Shionogi as an anti-influenza agent for treatment of influenza A and influenza B flu. Baloxavir marboxil is an orally available small molecule inhibitor of the cap-dependent endonuclease. Baloxavir was discovered by rational molecular design based on the two-metal pharmacophore concept for dolutegravir (DTG), a strand transfer inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integrase. Baloxavir potently and selectively inhibits the cap-dependent endonuclease within the polymerase PA subunit of influenza A and B viruses. In February 2018, baloxavir received its first global approval in Japan for the treatment of influenza A or B virus infections. Phase III development is underway in the USA, EU and other countries for this indication.The drug blocks influenza virus proliferation by inhibiting the initiation of mRNA synthesis. In clinical trials, single doses of Baloxavir profoundly decrease viral titers as well as alleviating influenza symptoms.
References: [1]. Frederick G Hayden, et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N Engl J Med. 2018 Sep 6;379(10):913-923.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 571.55 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₂₇H₂₃F₂N₃O₇S |
| CAS No. | 1985606-14-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 33.33 mg/mLr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
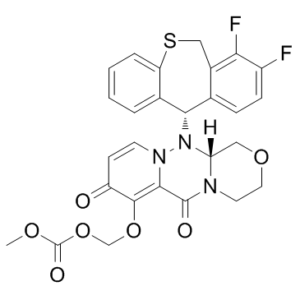
| SMILES Code | O=C(OCOC(C(C=C1)=O)=C(N1N([C@@H]2C3=CC=CC=C3SCC4=C(F)C(F)=CC=C24)[C@@]5([H])N6CCOC5)C6=O)OC |
| Synonyms | Trade name Xofluza; Baloxavir acid; BXA; Baloxavir marboxil; S-033188; S 033188; S033188 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Baloxavir marboxil (also known as BXM or S-033188) is the prodrug of Baloxavir (trade name Xofluza; also known as Baloxavir acid, BXA,or S-033447). It is an orally available small molecule inhibitor of the cap-dependent endonuclease developed by Roche and Shionogi. Baloxavir was discovered by rational molecular design based on the two-metal pharmacophore concept for dolutegravir (DTG), a strand transfer inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integrase. Baloxavir potently and selectively inhibits the cap-dependent endonuclease within the polymerase PA subunit of influenza A and B viruses. In February 2018, baloxavir received its first global approval in Japan for the treatment of influenza A or B virus infections. Phase III development is underway in the USA, EU and other countries for this indication.The drug blocks influenza virus proliferation by inhibiting the initiation of mRNA synthesis. In clinical trials, single doses of Baloxavir profoundly decrease viral titers as well as alleviating influenza symptoms. PA I38T substitution is a major pathway for reduced susceptibility to BXA, with 30- to 50-fold and 7-fold EC50changes in A and B viruses, respectively. The viruses harboring the I38T substitution show severely impaired replicative fitness in cells, and correspondingly reduced endonuclease activity in vitro. Kinase Assay: Oseltamivir acid was serially diluted in MES assay buffer [32.5 mmol/L MES and 4 mmol/L CaCl2 in DW (pH 6.5 adjusted with 4 N NaOH)]. To prepare NA enzyme solution, virus stocks were inactivated by 0.1% NP-40, and diluted with MES assay buffer. Ten μL of the oseltamivir acid solution and 10 μL of the NA enzyme solution were mixed and incubated at 37 °C for 30 minutes, followed by addition of 30 μL of 100 μmol/L 2′-(4-Methylumbelliferyl)-α-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid sodium salt hydrate (MUNANA; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.). The reaction mixtures were incubated at 37 °C for 60 minutes, and the reaction was stopped by addition of 150 μL of stop solution [0.1 mol/L glycine and 25% ethanol (pH 10.7 adjusted with 4 N NaOH)]. The fluorescence intensity was measured with a microplate reader EnVision 2103 (PerkinElmer Inc.) at excitation wavelength of 355 nm and an emission wavelength of 460 nm, followed by calculation of IC50 values with XLfit software. FC was calculated by dividing IC50 of each tested virus to IC50 of the cognate wild-type virus. Cell Assay: Canine kidney MDCK cells were obtained from European Collection of Cell Cultures. Human quasi-diploid tumor RPMI2650 and human embryonic kidney 293 T cells were provided by American Type Culture Collection. MDCK and RPMI2650 cells were maintained in minimal essential medium (MEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 µg/mL kanamycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). 293 T cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with 10% FBS and 100 µg/mL kanamycin. Eight plasmids-based reverse genetics technique was employed to generate recombinant viruses as described. The plasmid set of rgA/WSN/33 (H1N1) and empty vector pHW2000 were provided by Dr. Robert Webster at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. The plasmids for the generation of rgA/Victoria/3/75 and rgB/Maryland viruses were constructed with the pHW2000 by standard molecular biology techniques. The primer sequences used are available upon request. Co-culture of MDCK and 293 T cells were transfected with the eight plasmids and incubated 48 to 72 hours, followed by propagation of the viruses in MDCK cells. The PA sequences of the recombinant viruses were verified by Sanger sequencing. Viral titers were determined by standard tissue culture infectious dose (TCID)50 assay or plaque-forming unit (PFU) assay in MDCK cells. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In clinical trials, single doses of Baloxavir profoundly decrease viral titers as well as alleviating influenza symptoms. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.7496 mL | 8.7481 mL | 17.4963 mL | 34.9926 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3499 mL | 1.7496 mL | 3.4993 mL | 6.9985 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1750 mL | 0.8748 mL | 1.7496 mL | 3.4993 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0875 mL | 0.4374 mL | 0.8748 mL | 1.7496 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































