This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5g | $250 | Check With Us |
| 10g | $450 | Check With Us |
| 20g | $675 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V1979 CAS #: 527-73-1 Purity ≥ 98%
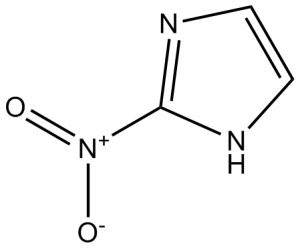
Description: Azomycin (2-Nitroimidazole) is an antimicrobial antibiotic extracted from a strain of Nocardia mesenterica and an unidentified Streptomyces. Azomycin is active against aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The structure of azomycinis a 2-nitroimidazole. Reduction of azomycin abolish the bacteriostatic activities. Also the closely related analog, 4-nitroimidazole does not exhibit bacteriostatic effects.
References: [1]. Shoji JH, et al. Isolation of azomycin from Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1989 Oct;42(10):1513-4.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 113.07 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H3N3O2 |
| CAS No. | 527-73-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: > 10 mMr |
| Water: NAr | |
| Ethanol: NA | |
| SMILES Code | O=[N+]([O-])C1=NC=CN1 |
| Synonyms | 2-Nitroimidazole |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Azomycin is an antibiotic which can be active against aerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is found that Azomycin is also active against a variety of anaerobic bacteria. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 8.8441 mL | 44.2204 mL | 88.4408 mL | 176.8816 mL |
| 5mM | 1.7688 mL | 8.8441 mL | 17.6882 mL | 35.3763 mL |
| 10mM | 0.8844 mL | 4.4220 mL | 8.8441 mL | 17.6882 mL |
| 20mM | 0.4422 mL | 2.2110 mL | 4.4220 mL | 8.8441 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































