This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $150 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $250 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $625 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V1973 CAS #: 65710-07-8 Purity ≥ 98%
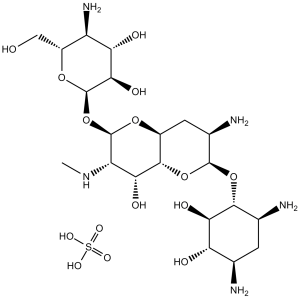
Description: Apramycin (also known as Ai3-29795; Nebramycin II) is a broad spectrum and aminoglycoside class of antibiotic, which binds to the deep groove of the RNA. Apramycin consumption at farm level is most probably driving the increasing occurrence of apramycin/gentamicin cross-resistant [aac(3)-IV positive] E. coli in diseased pigs and healthy finishers at slaughter. Apramycin inhibits A. pleuropneumoniae FMV 87-682 with MIC50 of 8 mg/L. Apramycin (1/4 MIC) in the medium decreases the rate of growth of the bacterial strains tested, and causes the postantibiotic effect (PAE) up to 5 hours.
References: [1]. O'Connor S, et al. Apramycin, a unique aminocyclitol antibiotic. J Org Chem. 1976 Jun 11;41(12):2087-92.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 637.66 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H41N5O11.xH2O4S |
| CAS No. | 65710-07-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: <1 mg/mLr |
| Water: 100 mg/mL (156.82 mM)r | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| SMILES Code | O[C@H]1[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H](NC)[C@@H](O)[C@]3([H])[C@@](C[C@@H](N)[C@@H](O[C@H]4[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](N)C[C@@H]4N)O3)([H])O2)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](N)[C@@H]1O.O=S(O)(O)=O |
| Synonyms | Ai3-29795; Ai3 29795; Ai 3-29795; Apramycin sulphate; Nebramycin II |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Apramycin consumption at farm level is most probably driving the increasing occurrence of apramycin/gentamicin cross-resistant [aac(3)-IV positive] E. coli in diseased pigs and healthy finishers at slaughter. Apramycin inhibits A. pleuropneumoniae FMV 87-682 with MIC50 of 8 mg/L. Apramycin (1/4 MIC) in the medium decreases the rate of growth of the bacterial strains tested, and causes the postantibiotic effect (PAE) up to 5 hours. Apramycin significantly reduces the haemolytic activity of A. pleuropneumoniae and affects the capsular material production of this isolate and of one isolate of P. multocida (type A). Apramycin induces translation errors, as assayed by incorporation of leucine, isoleucine and serine, although this effect occurs only to a limited extent, in cell-free systems from Escherichia coli programmed with poly(U). Apramycin inhibits the translocation step of protein synthesis both in vivo, in protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium, and in vitro, in cell-free systems from E. coli. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Apramycin (225 mg/L) totally suppresses mortality and significantly reduces Salmonella excretion in comparison with non-treated chicks. | |
| Animal model | Chicks | |
| Dosages | 225 mg/L |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.5682 mL | 7.8412 mL | 15.6823 mL | 31.3647 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3136 mL | 1.5682 mL | 3.1365 mL | 6.2729 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1568 mL | 0.7841 mL | 1.5682 mL | 3.1365 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0784 mL | 0.3921 mL | 0.7841 mL | 1.5682 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































