This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $850 | In Stock |
| 1g | $1350 | In Stock |
| 5g | $2025 | In Stock |
Cat #: V0415 CAS #: 1044870-39-4 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Apabetalone (also known as RVX-208, RVX000222) is a novel and potent inhibitor of BET (Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal) bromodomain (BD) with potential anti-inflammatory activity and the potential to be used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 370.4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H22N2O5 |
| CAS No. | 1044870-39-4 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 74 mg/mL (199.8 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| Solubility In Vivo | 0.5% CMC Na (1N HCl, PH 2.5-3.0): 8 mg/mL |
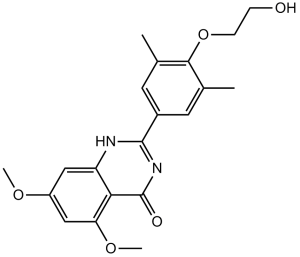
| SMILES Code | O=C1NC(C2=CC(C)=C(OCCO)C(C)=C2)=NC3=C1C(OC)=CC(OC)=C3 |
| Synonyms | RVX-000222; RVX208; RVX 000222; RVX 208; RVX000222; RVX-208; Apabetalone |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Apabetalone (RVX-208) competes with binding of an acetylated histone peptide to tandem BD1 BD2 protein constructs of the four BET proteins, with IC50s between 0.5 and 1.8 µM. Apabetalone increases the production of ApoA-I in hepatocytes in vitro, which results in increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Apabetalone selectively binds to bromodomains of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra Terminal) family, competing for a site bound by the endogenous ligand, acetylated lysine, and that this accounts for its pharmacological activity. Apabetalone increases Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) production through an epigenetic mechanism and suggests that BET inhibition may be a promising new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apabetalone increases ApoA-I expression in liver cells. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Apabetalone (RVX-208) competes with binding of an acetylated histone peptide to tandem BD1 BD2 protein constructs of the four BET proteins, with IC50s between 0.5 and 1.8 µM. Apabetalone increases the production of ApoA-I in hepatocytes in vitro, which results in increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Apabetalone selectively binds to bromodomains of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra Terminal) family, competing for a site bound by the endogenous ligand, acetylated lysine, and that this accounts for its pharmacological activity. Apabetalone increases Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) production through an epigenetic mechanism and suggests that BET inhibition may be a promising new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apabetalone increases ApoA-I expression in liver cells. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.6998 mL | 13.4989 mL | 26.9978 mL | 53.9957 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5400 mL | 2.6998 mL | 5.3996 mL | 10.7991 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2700 mL | 1.3499 mL | 2.6998 mL | 5.3996 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1350 mL | 0.6749 mL | 1.3499 mL | 2.6998 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































