ACHP Hydrochloride
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $1150 | Check With Us |
| 200mg | $1725 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $2910 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V30592 CAS #: 406209-26-5 Purity ≥ 99%
Description: ACHP hydrochloride (also known as IKK-2 Inhibitor VIII), the hydrochloride salt of ACHP, is a novel, highly potent and selective IKK-β inhibitor with IC50 of 8.5 nM.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 400.90 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H25ClN4O2 |
| CAS No. | 406209-26-5 |
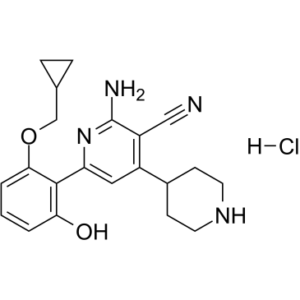
| SMILES Code | OC1=C(C2=CC(C3CCNCC3)=C(C#N)C(N)=N2)C(OCC4CC4)=CC=C1.Cl |
| Synonyms | IKK-2 Inhibitor VIII |
| Protocol | In Vitro | ACHP Hydrochloride (Compound 4j) exhibits potent IKK-β inhibitory (IC50: 8.5 nM) and cellular activities (IC50=40 nM, in A549 cells). ACHP moderately inhibits IKK-α with an IC50 of 250 nM but exhibits good selectivity towards other kinases, such as IKK3, Syk and MKK4 (IC50>20,000 nM). Moreover, ACHP demonstrates quite potent activity in various cellular assays. ACHP inhibits NF-κB-dependent reporter gene activation in TNFα-activated HEK293 cells and PMA/calcium ionophore-activated Jurkat T cells. ACHP fails to inhibit PMA-induced AP-1 activation in MRC-5 cells and PMA/calcium ionophore induced NF-κB dependent reporter gene transcription in Jurkat cells even at concentrations exceeding 10 μM. ACHP selectively interferes with the NF-κB signaling cascade by inhibition of IKK-β in living cells. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | ACHP (Compound 4j) is orally bioavailable in mice and rats and demonstrates significant in vivo activity in anti-inflammatory models (arachidonic acid-induced mouse ear edema model). ACHP has reasonable aqueous solubility (0.12 mg/mL in pH 7.4 isotonic buffer) and excellent Caco-2 permeability (Papp 62.3×10-7 cm/s), and demonstrates orally bioavailability in mice (BA: 16%) and rats (BA: 60%). The favourable bioavailability of ACHP in rats is likely due to its low clearance (0.33 L/h/kg). In an acute inflammation model, ACHP exhibits oral efficacy at 1 mg/kg in a dose-dependent manner. |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.4944 mL | 12.4719 mL | 24.9439 mL | 49.8878 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4989 mL | 2.4944 mL | 4.9888 mL | 9.9776 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2494 mL | 1.2472 mL | 2.4944 mL | 4.9888 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1247 mL | 0.6236 mL | 1.2472 mL | 2.4944 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































