This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
Cat #: V3809 CAS #: 1795232-22-2 Purity ≥ 98%
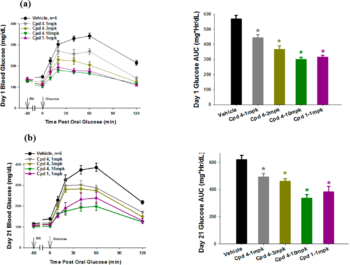
Description: LY3104607 is a potent, selective and orally available G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 (GPR40) agonist with potential antidiabetic application. It has optimized pharmacokinetic properties to support once daily oral treatment in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. LY3104607 demonstrated functional potency and glucose-dependent insulin secretion (GDIS) in primary islets from rats. Potent, efficacious, and durable dose-dependent reductions in glucose levels were seen during glucose tolerance test (GTT) studies. Low clearance, volume of distribution, and high oral bioavailability were observed in all species. The combination of enhanced pharmacology and pharmacokinetic properties supported further development of this compound as a potential glucose-lowering drug candidate.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 439.52 |
|---|---|
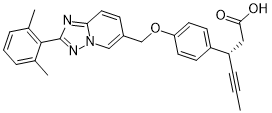
| Molecular Formula | C27H25N3O3 |
| CAS No. | 1795232-22-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mM |
| Water: <1mg/mL | |
| Ethanol: <1mg/mL | |
| Synonyms | LY3104607; LY-3104607; LY 3104607 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: LY3104607 is a potent, selective and orally available G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 (GPR40) agonist with potential antidiabetic application. It has optimized pharmacokinetic properties to support once daily oral treatment in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. LY3104607 demonstrated functional potency and glucose-dependent insulin secretion (GDIS) in primary islets from rats. Potent, efficacious, and durable dose-dependent reductions in glucose levels were seen during glucose tolerance test (GTT) studies. Low clearance, volume of distribution, and high oral bioavailability were observed in all species. The combination of enhanced pharmacology and pharmacokinetic properties supported further development of this compound as a potential glucose-lowering drug candidate. Kinase Assay: All in vitro assays including binding, calcium flux, β-arrestin agonist, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) α, δ, and γ assays were described previously in detail. The use of animals was in accordance with international guidelines (NIH 85-23) and was approved by the local animal ethics committee at Lilly Research Laboratories. Cell Assay: Glucose-Dependent Insulin Secretion (GDIS) in Rat Islet. GDIS assays were performed in primary islets. Pancreatic islets of Langerhans were isolated from male SD (Sprague−Dawley) rats by collagenasedigestion and Histopaque density gradient separation. The islets were cultured overnight in RPMI-1640 medium with GlutaMAXn to facilitate recovery from the isolation process. Insulin secretion was determined using 90 min incubation in EBSS (Earle’s Balances Salt Solution) buffer in a 48-well plate. Islets were first preincubated in EBSS with 2.8 mM glucose for 60 min, then transferred to a 48-well plate (four islets/well) containing 150 μL of 2.8 mM glucose, and incubated with 150 μL of EBSS with 2.8 or 11.2 mM glucose in the presence or absence of test compounds for 90 min. The buffer was removed from the wells at the end of the incubation period and assayed for insulin levels using a rat insulin ELISA kit (Mercodia). |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) in Zucker ( fa/fa) Rats. OGTTs were performed in male Zucker ( fa/fa) rats (10 weeks of age), a rodent model of insulin resistance, after 1 and 21 days of oral administration. Compounds were administered orally at various doses to provide a dose−response efficacy curve. Compound 1 served as the positive control and reference standard for the study. OGTTs were performed 1 h after compound administration with blood samples taken for determination of glucose and insulin levels at 0, 10, 20, 40, and 60 min post glucose administration (2g/kg). | |
| Animal model | Zucker ( fa/fa) Rats |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.2752 mL | 11.3760 mL | 22.7521 mL | 45.5042 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4550 mL | 2.2752 mL | 4.5504 mL | 9.1008 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2275 mL | 1.1376 mL | 2.2752 mL | 4.5504 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1138 mL | 0.5688 mL | 1.1376 mL | 2.2752 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.