This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
Cat #: V3736 CAS #: 1164153-37-0 Purity ≥ 98%
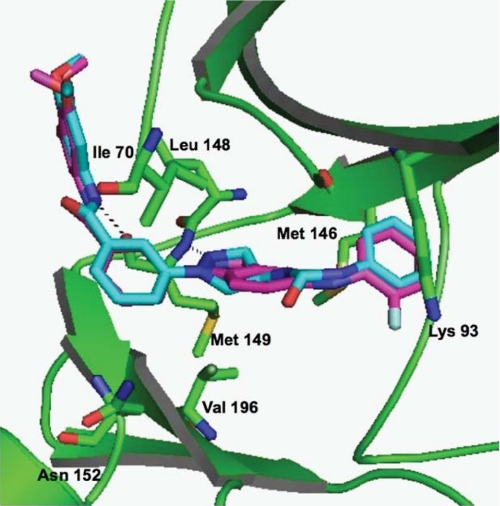
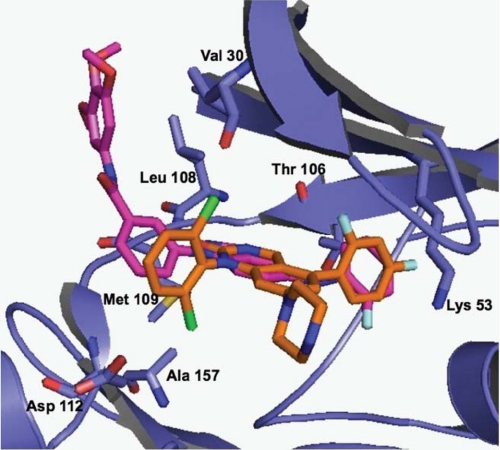
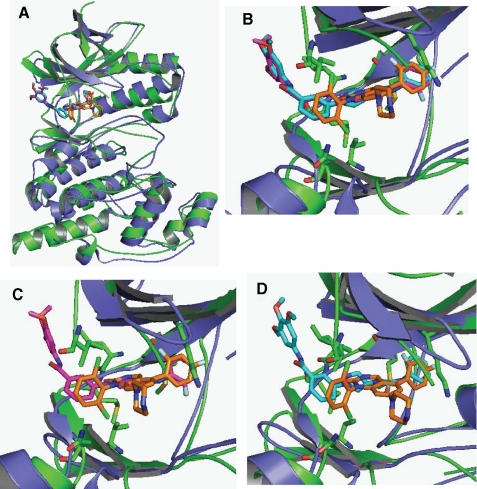
Description: SR-3737, an amino pyrazole and indazole analog, is a potent JNK inhibitor but is non-selective for JNK3 (IC50 = 12 nM) and p38 (IC50 = 3 nM). c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3alpha1 (JNK3alpha1) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase family member expressed primarily in the brain that phosphorylates protein transcription factors, including c-Jun and activating transcription factor-2 (ATF-2) upon activation by a variety of stress-based stimuli.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 512.54 |
|---|---|
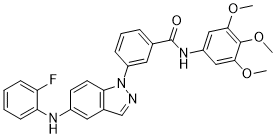
| Molecular Formula | C29H25FN4O4 |
| CAS No. | 1164153-37-0 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mM |
| Water: | |
| Ethanol: | |
| Synonyms | SR-3737; SR 3737; SR3737 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: SR-3737, an amino pyrazole and indazole analog, is a potent JNK inhibitor but is non-selective for JNK3 (IC50 = 12 nM) and p38 (IC50 = 3 nM). c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3alpha1 (JNK3alpha1) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase family member expressed primarily in the brain that phosphorylates protein transcription factors, including c-Jun and activating transcription factor-2 (ATF-2) upon activation by a variety of stress-based stimuli. Kinase Assay: Homogeneous Time-resolved Fluorescence Assay—Enzyme inhibition studies were performed in 384-well polystyrene homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence plates (Grainier) for 15 min at ambient temperature (∼22 °C) with 0.2 μm biotinylated FL-ATF-2, 1 μm ATP, 0.3 nm activated JNK3α1 (with a control in the absence of kinase for determining the basal signal) in 10-μl volumes containing the final concentrations of the following: 50 mm Hepes, pH 7.0, 2.5 mm MgCl2, 0.1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 1 mm dl-dithiothreitol, 0.01% Triton X-100 (all from Sigma-Aldrich), and 5% DMSO (with or without compound). A 10-point titration of all compounds was carried out in 3-fold dilutions from 10 pm to 2000 nm. After 15 min, the kinase reaction was terminated by addition of 10 μl of quenching solution (50 mm Hepes, pH 7.0, with 14 mm EDTA, 0.01% Triton X-100, 400 mm KF (all from Sigma-Aldrich)). The detection reagents, streptavidin-xlAPC (200 nm) and europium cryptate-labeled rabbit polyclonal anti-phospho-ATF-2 (0.43 ng/well), were from Cis-Bio. The homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence signal was detected using a viewlux plate reader (PerkinElmer Life Sciences) 1 h post-quenching. The data from four different experiments were averaged and presented as the mean ± S.D. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the equation for a four-parameter logistic. p38 enzyme inhibition assays were performed identically to the JNK3 assays with the exception that the reaction time was 30 min, ATP = 11 μm, and p38 (Millipore) = 0.625 nm. Cell Assay: Cell-based Assays Measuring JNK Activity—INS-1 β-pancreatic cells were plated in a 96-well tissue culture plate at 3.5 × 104 cells/well (Corning) in a media containing RPMI 1640 (± glutamine (2 mm)) and 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen) and incubated overnight at 37 °C in 5% CO2. An assay plate was prepared by coating a 96-half-well plate (Costar) with 50 μl/well p-c-Jun capture antibody (Cell Signaling). Cells were incubated with 4 mm streptozotocin containing various concentrations of potential inhibitor dissolved in DMSO for 3 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. After treatment the media was removed, and the cells were washed in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline. The phosphate-buffered saline was removed, and the cells were lysed in ice-cold lysis buffer (100 μl/well) containing 1× protease (Roche Applied Science) and 1× phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma). Lysates were transferred to the corresponding well of the blocked assay plate, covered tightly, and incubated 16 h at 4 °C. The c-Jun detection antibody (100× dilution), and the secondary anti-mouse coupled horseradish peroxidase (1000× dilution) were purchased from Cell Signaling. Inhibition of signal was quantified using TMB substrate (BioFX Laboratories) and read on a microplate reader at an absorbance of 450 nm. IC50 values were determined using a four-parameter logistic and a 10-point dilution curve for each of the inhibitors covering four orders of magnitude of inhibitor concentration. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.9511 mL | 9.7553 mL | 19.5107 mL | 39.0213 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3902 mL | 1.9511 mL | 3.9021 mL | 7.8043 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1951 mL | 0.9755 mL | 1.9511 mL | 3.9021 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0976 mL | 0.4878 mL | 0.9755 mL | 1.9511 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.