This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
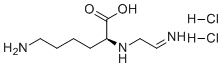
Cat #: V14164 CAS #: 159190-45-1 Purity ≥ 99%
Description: L-NIL diHCl (dihydrochloride) is a novel and potent inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) (IC50 = 3.3 μM for miNOS) with anti-inflammatory activity. L-NIL has an IC50 of 3.3 microM for miNOS compared to an IC50 of 92 microM for rat brain constitutive NOS indicating that L-NIL is 28-fold more selective for inducible NOS. L-N5-(1-Iminoethyl)ornithine (L-NIO), which differs from L-NIL by having one less methylene group, has very similar potency for inducible NOS, but lacks selectivity. DL-N7-(1-Iminoethyl)homolysine was also synthesized and found to be substantially less potent than L-NIL or L-NIO, with intermediate selectivity for inducible NOS. These data suggest that L-NIL may be useful as a selective inhibitor of inducible NOS for determining the role of this enzyme in disease models.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 260.15 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H19Cl2N3O2 |
| CAS No. | 159190-45-1 |
| Synonyms | L-NIL HCl |
| Protocol | In Vitro | L-NIL produces a concentration-dependent inhibition of both the mouse inducible NOS (miNOS) and the rat brain constitutive NOS (rcNOS) and is considerably more potent for miNOS. The IC50 values for L-NIL with miNOS and rcNOS are 3.3 and 92 pM, respectively, indicating that L-NIL is 28-fold more selective for miNOS. In addition, L-NIL has approximately 6-fold greater potency for miNOS than either L-NMA or L-NNA[2]. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | L-NIL (10 and 30 mg/kg, IP) prevents the inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy induced by renal IR in mice[1]. Animal Model: Adult male Balb/c (20-25 g)[1]. Dosage: 10 and 30 mg/kg. Administration: Intraperitoneally at the end of CLP and at 6 h after sepsis induction. Result: Led to a negligible increase in plasma NGAL compared to sham mice. Led to a significant decrease in both TLR4 and IL1βprotein contents and clusterin transcript. Showed an increase in NFAT5 mRNA levels, as compared with mice treated with vehicle. Promoted a decrease in AR protein expression, as compared with animals treated with vehicle. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 3.8439 mL | 19.2197 mL | 38.4394 mL | 76.8787 mL |
| 5mM | 0.7688 mL | 3.8439 mL | 7.6879 mL | 15.3757 mL |
| 10mM | 0.3844 mL | 1.9220 mL | 3.8439 mL | 7.6879 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1922 mL | 0.9610 mL | 1.9220 mL | 3.8439 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































