This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5mg | $220 | To Be Confirmed |
| 10mg | $340 | To Be Confirmed |
| 25mg | $600 | To Be Confirmed |
| 50mg | $899 | To Be Confirmed |
| 100mg | $1350 | To Be Confirmed |
| 250mg | $2380 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V2719 CAS #: 1522418-41-2 Purity ≥ 98%
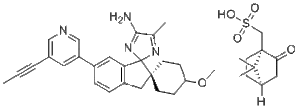
Description: Lanabecestat camsylate (formerly known as AZD-3293; LY3314814), the camsylate salt of Lanabecestat, is a BACE inhibitor that inhibits beta-secretase 1 cleaving enzyme (BACE) with a Ki of 0.4 nM. AZD3293 displayed significant dose- and time-dependent reductions in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain concentrations of Aβ40, Aβ42, and sAβPPβ. The in vitro potency of AZD3293 was demonstrated in several cellular models, including primary cortical neurons. In vivo in mice, guinea pigs, and dogs, AZD3293 displayed significant dose- and time-dependent reductions in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain concentrations of Aβ40, Aβ42, and sAβPPβ. The in vitro potency of AZD3293 in mouse and guinea pig primary cortical neuronal cells was correlated to the in vivo potency expressed as free AZD3293 concentrations in mouse and guinea pig brains. In mice and dogs, the slow off-rate from BACE1 may have translated into a prolongation of the observed effect beyond the turnover rate of Aβ. The preclinical data strongly support the clinical development of AZD3293, and patients with AD are currently being recruited into a combined Phase 2/3 study to test the disease-modifying properties of AZD3293.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 644.83 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H44N4O5S |
| CAS No. | 1522418-41-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: > 80 mg/mL |
| Water: N/A | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Solubility In Vivo | Lanabecestat camsylate; Lanabecestat; LY3314814; AZD3293 camsylate; LY-3314814 camsylate; AZD-3293; LY 3314814; AZD 3293 |
| Synonyms | O=S(C[C@@]1(C2(C)C)C(C[C@@]2([H])CC1)=O)(O)=O.NC(C(C)=N3)=NC43C5=C(C=CC(C6=CC(C#CC)=CN=C6)=C5)C[C@]74CCC(OC)CC7 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: AZD3293 is a potent, highly permeable, orally active, blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetrating, BACE1 inhibitor with unique slow off-rate kinetics. When the potency of AZD3293 with respect to secretion of Aβ40 and sAβPPβ is studied in a range of cellular models, the compound displays pM potency in primary neuron cultures from mice and guinea pigs and in SH-SY5Y cells over-expressing AβPP (IC50 = 610 pM, 310 pM, and 80 pM, respectively). AZD3293 is also tested in a panel of more than 350 in vitro radioligand binding and enzyme activity assays, covering a diverse range of receptors, ion channels, transporters, kinases, and enzymes, up to a concentration of 10μM of AZD3293. A few significant responses are observed, but these had at least a 1,000-fold selectivity against BACE1, thus indicating specificity to BACE1. The off-rate of AZD3293 has an estimated t1/2 of approximately 9 h. Kinase Assay: Lanabecestat (formerly known as AZD3293 and LY3314814), is a novel potent, orally bioactive, highly permeable, brain-penetreable inhibitor of beta-secretase 1 cleaving enzyme (BACE) with a Ki of 0.4 nM. AZD3293 displayed significant dose- and time-dependent reductions in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain concentrations of Aβ40, Aβ42, and sAβPPβ. Cell Assay: The cells [SH-SY5Y, SH-SY5Y overexpressing wild type AβPP, HEK293 cells overexpressing AβPP with the Swedish mutation (K595N/M596L), N2A cells, and primary cortical neurons isolated from fetal C57BL/6 mice (E16) or Dunkin-Hartley guinea pigs (E25-27)] are incubated with different AZD3293 concentrations for 5 to 16 h, and the release of sAβPPβ, Aβ1-40, Aβ1-42, or sAβPPα into the medium is analyzed using specific commercial ELISA or kits from Meso Scale Discovery. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In vivo in mice, guinea pigs, and dogs, AZD3293 displays significant dose- and time-dependent reductions in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain concentrations of Aβ40, Aβ42, and sAβPPβ. In the dog PK study, the bioavailability of AZD3293 is determined to be 80% (F = 0.8). The preclinical data strongly support the clinical development of AZD3293, and patients with AD are currently being recruited into a combined Phase 2/3 study to test the disease-modifying properties of AZD3293. | |
| Animal model | C57BL/6 mice |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.5508 mL | 7.7540 mL | 15.5080 mL | 31.0159 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5508 mL | 3.1016 mL | 6.2032 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1551 mL | 0.7754 mL | 1.5508 mL | 3.1016 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0775 mL | 0.3877 mL | 0.7754 mL | 1.5508 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































