This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5g | $350 | To Be Confirmed |
| 10g | $500 | To Be Confirmed |
| 20g | $750 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V5283 CAS #: 67-97-0 Purity ≥ 98%
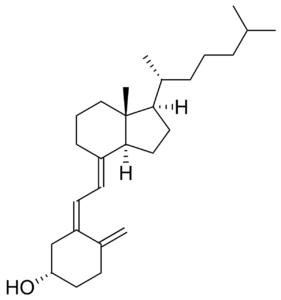
Description: Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3; Colecalciferol), a secosteroid (a steroid molecule with one ring open), is a naturally occuring form of vitamin D; Upon metabolic activation, cholecalciferol is converted to the active form, 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3, which induces cell differentiation and prevents proliferation of cancer cells.
References: Nazik Al-Hashimi, et al. Cholecalciferol
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 384.64 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H44O |
| CAS No. | 67-97-0 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| SMILES Code | C[C@H](CCCC(C)C)[C@H]1CC[C@@H]\2[C@@]1(CCC/C2=C\C=C/3\C[C@H](CCC3=C)O)C |
| Synonyms | Cholecalciferol; Vitamin D3; Ricketon; Trivitan; Vigantol; Vigorsan; Deparal; Calciol; Colecalciferol; Arachitol; Activated 7-dehydrocholesterol; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Vitamin D3 is an inactive vitamin D molecule in vivo. Vitamin D3 undergoes two hydroxylation processes to activate it. Vitamin D3 is first hydroxylated in the liver to form the circulating prohormone 25-hydroxy vitamin D3 [25(OH)D3] by the enzyme 25-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) and probably also by other enzymes (e.g., CYP2R1). The second hydroxylation occurs in the kidneys via the enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase, yielding 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol), which is the biologically active form of vitamin D. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Cholecalciferol (oral gavage; 5 mg/kg; 7 days) potentiates the CCl4 toxicity only in the liver, as indicated by plasma levels of ALT and AST, biochemical markers of hepatic damage. It significantly increases renal calcium levels in mice, but renal calcium content does not differ significantly between mice. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.5998 mL | 12.9992 mL | 25.9983 mL | 51.9967 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5200 mL | 2.5998 mL | 5.1997 mL | 10.3993 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2600 mL | 1.2999 mL | 2.5998 mL | 5.1997 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1300 mL | 0.6500 mL | 1.2999 mL | 2.5998 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































