This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 25g | $450 | Check With Us |
| 50g | $700 | Check With Us |
| 100g | $1770 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V1003 CAS #: 475207-59-1 Purity ≥ 98%
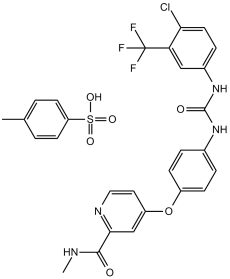
Description: Sorafenib Tosylate (BAY439006; BAY-439006; BAY549085; BAY-549085; Nexavar; SFN), the tosylate salt of Sorafenib which is an approved anticancer medication, is a potent multi-kinase inhibitor of Raf-1, B-Raf and VEGFR-2 with potential antineoplastic activity.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 637.03 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H16ClF3N4O3.C7H8O3S |
| CAS No. | 475207-59-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 127 mg/mL (199.4 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mL (slightly soluble or insoluble)r | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| SMILES Code | O=C(NC)C1=NC=CC(OC2=CC=C(NC(NC3=CC=C(Cl)C(C(F)(F)F)=C3)=O)C=C2)=C1.O=S(C4=CC=C(C)C=C4)(O)=O |
| Synonyms | Sorafenib tosylate; Nexavar; SFN; BAY 439006; BAY439006; BAY-439006; BAY 439006 Tosylate Salt; BAY 549085; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Sorafenib Tosylate also inhibits BRAFwt (IC50=22 nM), BRAFV599E (IC50=38 nM), VEGFR-2 (IC50=90 nM), VEGFR-3 (IC50=20 nM), PDGFR-β (IC50=57 nM), c-KIT (IC50=68 nM), and Flt3 (IC50=58 nM) in biochemical assays. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Sorafenib Tosylate (10, 30, 50 and 100 mg/kg, orally) treatment inhibits the tumor growth of 06-0606 and 10-0505 xenografts in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.01). The growth rate of 06-0606 and 10-0505 xenografts is also significantly reduced by Sorafenib. The weights of 06-0606 tumors in mice that are treated with Sorafenib 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg are approximately 13% and 5% of the controls, respectively. 50 mg dose of Sorafenib significantly inhibits tumor growth in mice with lines 5-1318, 26-1004 and 10-0505 (P<0.01). For 50 mg dose, the T/C ratio, where T and C are the median weight (mg) of Sorafenib- and vehicle-treated tumors at the end of the treatment, respectively, for 06-0606, 26-1004, 5-1318, and 10-0505 xenografts is 0.13, 0.10, 0.12 and 0.49, respectively. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.5698 mL | 7.8489 mL | 15.6978 mL | 31.3957 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3140 mL | 1.5698 mL | 3.1396 mL | 6.2791 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1570 mL | 0.7849 mL | 1.5698 mL | 3.1396 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0785 mL | 0.3924 mL | 0.7849 mL | 1.5698 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































