This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 100mg | $1850 | Check With Us |
| 200mg | $2775 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $4650 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2085 CAS #: 1575596-29-0 Purity ≥ 98%
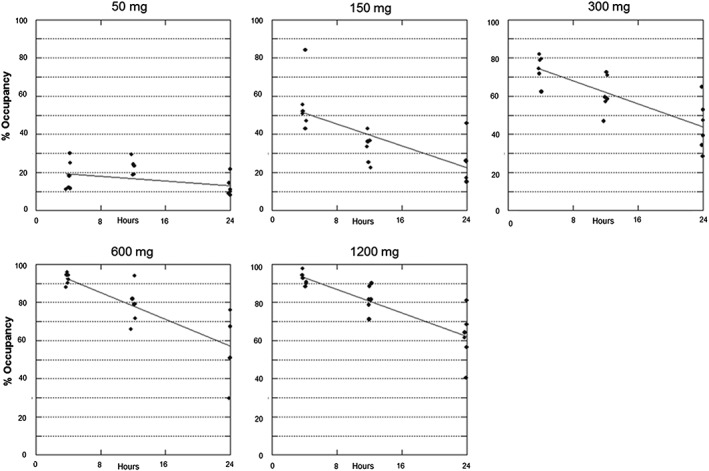
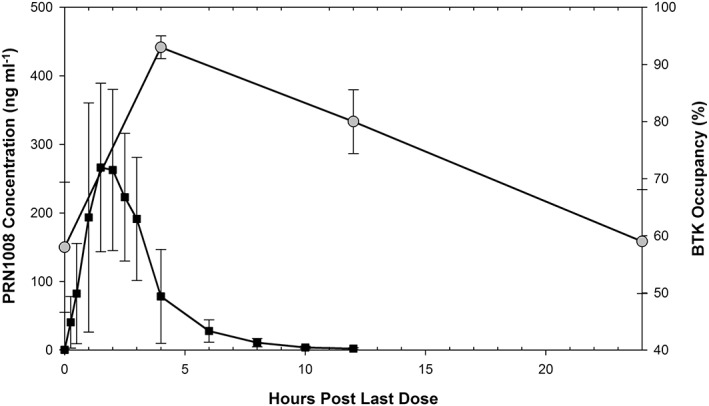
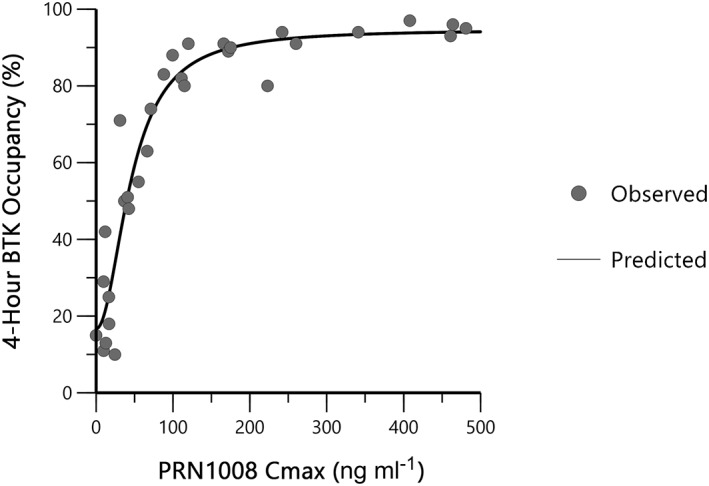
Description: Rilzabrutinib (PRN-1008) is a novel, highly potent, and reversible covalent inhibitor of BTK (Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase) being studied for treating rheumatoid arthritis. It inhibits BTK with an IC50 of 1.3 nM. BTK is a Tec family tyrosine kinase, is critical in immune pathways as an essential intracellular signaling element, participating in both adaptive and immune responses. PRN1008 was found to be very potent against BTK and highly selective when tested against a panel of 251 other kinases. Cysteine targeting of BTK by PRN1008 results in a slow off-rate demonstrated by retention of 79 ± 2% of binding to BTK in PBMC 18 hours after washing away the compound in vitro. PRN1008 was safe and well-tolerated following oral administration, and achieved high, sustained levels of BTK occupancy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PRN1008 is currently under Phase I development as a therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 665.77 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H40FN9O3 |
| CAS No. | 1575596-29-0 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 10 mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
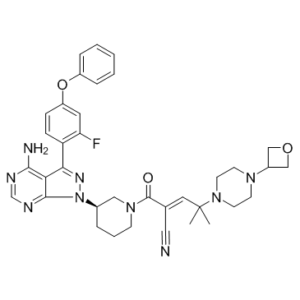
| SMILES Code | NC1=C2C(C3=C(C=C(OC4=CC=CC=C4)C=C3)F)=NN([C@H]5CN(CCC5)C(/C(C#N)=C/C(C)(N6CCN(C7COC7)CC6)C)=O)C2=NC=N1 |
| Synonyms | Rilzabrutinib; PRN-1008; PRN1008; PRN 1008 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: PRN1008 is a highly potent, reversible covalent inhibitor of BTK (Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase) with an IC50 of 1.3 nM. PRN1008 was found to be very potent against BTK and highly selective when tested against a panel of 251 other kinases. Cysteine targeting of BTK by PRN1008 results in a slow off-rate demonstrated by retention of 79 ± 2% of binding to BTK in PBMC 18 hours after washing away the compound in vitro. PRN1008 was safe and well-tolerated following oral administration, and achieved high, sustained levels of BTK occupancy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PRN1008 is currently under Phase I development as a therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis. Kinase Assay: PRN1008 is very potent against BTK (IC50=1.3±0.5 nM) and highly selective against a panel of 251 other kinases. Cysteine targeting of BTK by PRN1008 results in a slow off-rate demonstrated by retention of 79±2% of binding to BTK in PBMC 18 hours after washing away the compound in vitro. The covalent cysteine binding is completely reversible after denaturation of the target. Anti-IgM induces human B cell proliferation (10% serum) and B cell CD69 expression are inhibited by PRN1008 with IC50 of 5±2.4 nM and 123±38 nM, respectively Cell Assay: Anti-IgM induced human B cell proliferation (10% serum) and B cell CD69 expression (whole blood) were inhibited by PRN1008 with IC50 of 5 ± 2.4 nM and 123 ± 38 nM, respectively. PRN1008 did not block EGFR signaling in epithelial cells or TCR and calcium flux stimulated T cell activation. PRN1008 also did not block IL-4 stimulation of B cells and did not exhibit cytotoxicity in an epithelial cell line HCT-116. In addition, PRN1008 did not block antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in combination with anti-CD20 antibodies allowing for potential combination therapies. In vivo PRN1008 demonstrated enduring pharmacodynamic effects after the compound had cleared from circulation, consistent with extended target residence time. PRN1008 also reversed and completely suppressed collagen-induced arthritis in rats in a dose dependent manner which allowed correlation of target occupancy and disease modification. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In vivo PRN1008 demonstrates enduring pharmacodynamic effects after the compound has cleared from circulation, consistent with extended target residence time. PRN1008 also reverses and completely suppresses collagen-induced arthritis in rats in a dose dependent manner which allows correlation of target occupancy and disease modification[ | |
| Animal model | Rats with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model | |
| Dosages | 10, 20, 40 mg/kg |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.5020 mL | 7.5101 mL | 15.0202 mL | 30.0404 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3004 mL | 1.5020 mL | 3.0040 mL | 6.0081 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1502 mL | 0.7510 mL | 1.5020 mL | 3.0040 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0751 mL | 0.3755 mL | 0.7510 mL | 1.5020 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.