This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $989 | To Be Confirmed |
| 500mg | $1450 | To Be Confirmed |
| 1g | $2175 | To Be Confirmed |
Cat #: V3875 CAS #: 1207283-85-9 Purity ≥ 98%
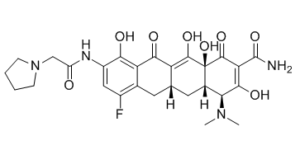
Description: Eravacycline (formerly known as TP-434; TP434; trade name: Xerava) is a novel fluorocycline with a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activity against panels of recently isolated aerobic and anaerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. It was approved by FDA in August 2018 to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections in patients 18 years of age and older. Eravacycline showed potent broad-spectrum activity against 90% of the isolates (MIC90) in each panel at concentrations ranging from ≤0.008 to 2 μg/ml for all species panels except those of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia (MIC90 values of 32 μg/ml for both organisms). The antibacterial activity of eravacycline was minimally affected by expression of tetracycline-specific efflux and ribosomal protection mechanisms in clinical isolates. Furthermore, eravacycline was active against multidrug-resistant bacteria, including those expressing extended-spectrum β-lactamases and mechanisms conferring resistance to other classes of antibiotics, including carbapenem resistance. Eravacycline has the potential to be a promising new intravenous (i.v.)/oral antibiotic for the empirical treatment of complicated hospital/health care infections and moderate-to-severe community-acquired infections.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 558.56 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₂₇H₃₁FN₄O₈ |
| CAS No. | 1207283-85-9 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: >10 mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| SMILES Code | O=C(NC(C(O)=C1C2=O)=CC(F)=C1C[C@@]3([H])C[C@@]4([H])[C@H](N(C)C)C(O)=C(C(N)=O)C ([C@@]4(O)C(O)=C32)=O)CN5CCCC5 |
| Synonyms | TP-434-046; TP-434; TP 434; TP434 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Eravacycline is potent antibiotic against A. baumannii, including isolates that are resistant to sulbactam, imipenem/meropenem, levofloxacin, and amikacin/tobramycin. Eravacycline shows greater activity than the comparators of the tetracycline class, levofloxacin, amikacin, tobramycin, and colistin. The eravacycline MIC50/90 values are 0.5/1 mg/L[1]. Eravacycline shows inhibitory effects on six E. coli with MICs ranging from 0.125 to 0.25 mg/L[2]. Eravacycline dihydrochloride is a synthetic antibiotic, with inhibits bacterial protein synthesis through binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Eravacycline displays broad spectrum activity against gram-negative bacteria in the panel except P. aeruginosa, as well as excellent activity against major gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Eravacycline also displays potent ribosomal inhibition[3]. Eravacycline shows potent broad-spectrum activity against 90% of the isolates (MIC90) in each panel at concentrations ranging from ≤0.008 to 2 μg/mL for all species panels except those of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cenocepacia (MIC90 values of 32 μg/mL for both organisms). Eravacycline is active against multidrug-resistant bacteria, including those expressing extended-spectrum β-lactamases and mechanisms conferring resistance to other classes of antibiotics, including carbapenem resistance[4]. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Mice are treated with two-fold increasing doses (range 3.125 to 50 mg/kg) of eravacycline every 12 hours. The mean fAUC/MIC magnitude associated with net stasis and 1-log kill endpoint are 27.97±8.29 and 32.60±10.85, respectively[2]. Eravacycline is active in multiple murine models of infection against clinically important Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. Eravacycline is efficacious in mouse septicemia models, demonstrating 50% protective dose values of ≤1 mg/kg of body weight once a day (q.d.) against Staphylococcus aureus, including tetracycline-resistant isolates of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), and Streptococcus pyogenes. The PD50 values against Escherichia coli isolates are 1.2 to 4.4 mg/kg q.d[5]. | |
| Animal model | Rats[3] Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters are determined in Sprague−Dawley rats. Animals are fasted overnight (minimum of 12 h) and given a single oral (10 mg/kg) or IV dose (1 mg/kg) of eravacycline followed by a sampling scheme for 24 h. Plasma and dosing solution concentrations are determined by TurboIonspray LC/MSMS analysis using appropriate standard curves. PK parameters are calculated by noncompartmental analysis. Mice[5] Eravacycline is formulated in sterile 0.9% saline. BALB/c mice are inoculated with 0.2 mL of prepared bacterial inoculum via intravenous injection to seed the kidney. Animals are administered antibiotics (eravacycline) at 10 mL/kg i.v. via the tail vein 12 and 24 h postinfection. Then the bacterial burden is determined. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.7903 mL | 8.9516 mL | 17.9032 mL | 35.8064 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3581 mL | 1.7903 mL | 3.5806 mL | 7.1613 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1790 mL | 0.8952 mL | 1.7903 mL | 3.5806 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0895 mL | 0.4476 mL | 0.8952 mL | 1.7903 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































