This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $320 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $550 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $1400 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2009 CAS #: 165800-03-3 Purity ≥ 98%
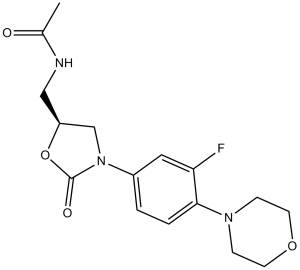
Description: Linezolid (also known as PNU-100766), a synthetic oxazolidinone antimicrobial, is an antibiotic used for the treatment of serious infections. Linezolid shows a wide spectrum against Gram-positive bacteria andmultidrug-resistant bacteria such as anaerobes, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococci, penicillin-resistant pneumococci and streptococcus. Linezolid inhibits initiation complex formation with either the 30S or the 70S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Linezolid inhibits complex formation with Staphylococcus aureus 70S tight-couple ribosomes.
References: [1]. Clemett D, Markham A. Linezolid. Drugs. 2000 Apr;59(4):815-27; discussion 828.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 337.35 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H20FN3O4 |
| CAS No. | 165800-03-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 67 mg/mL (198.6 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: 8 mg/mL (23.7 mM) | |
| Solubility In Vivo | 30% PEG400+0.5% Tween80+5% Propylene glycol: 30 mg/mL |
| SMILES Code | CC(=O)NC[C@H]1CN(C(=O)O1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)N3CCOCC3)F |
| Synonyms | PNU 100766; PNU-100766; PNU100766; U 100766; U-100766; U100766; Linezolid; Zyvox; Zyvoxid; Zyvoxam |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Linezolid inhibits initiation complex formation with either the 30S or the 70S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Linezolid inhibits complex formation with Staphylococcus aureus 70S tight-couple ribosomes. Linezolid is a potent inhibitor of cell-free transcription-translation in E. coli, exhibiting 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of 1.8 mM. Linezolid is an oxazolidinone, a new class of antibacterial agents with enhanced activity against pathogens. Linezolid MICs vary slightly with the test method, laboratory, and significance attributed to thin hazes of bacterial survival, but all workers find that the susceptibility distributions are narrow and unimodal, with MIC values between 0.5 and 4 mg/L for streptococci, enterococci and staphylococci. Linezolid entails mutation of the 23S rRNA that forms the binding site. Linezolid is an oxazolidinone whose mechanism of action involves inhibition of protein synthesis at a very early stage. Linezolid is added to 7H10 agar medium (Difco) supplemented with OADC (oleic acid, albumin, dextrose, and catalase) at 50°C to 56°C by doubling the dilutions to yield a final concentration of 0.125 μg/mL to 4 μg/mL. Linezolid shows excellent in vitro activity against all the strains tested (MICs ≤ 1 μg/ml), including those resistant to SIRE. Cell Assay: Linezolid was a potent inhibitor of cell-free transcription-translation in E. coli. IC50 was 1.8 mM. linezolid MICs vary slightly owing to the different test method and laboratory. The MIC values were between 0.5 and 4 mg/L for streptococci, enterococci and staphylococci. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Clinical Trials: Linezolid is fully bioavailable following oral administration, with maximum plasma linezolid concentrations achieved between 1 and 2 hours after oral administration. The elimination half-life of linezolid is 5–7 hours, and twice-daily administration of 400–600mg provides steady-state concentrations in the therapeutic range. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.9643 mL | 14.8214 mL | 29.6428 mL | 59.2856 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5929 mL | 2.9643 mL | 5.9286 mL | 11.8571 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2964 mL | 1.4821 mL | 2.9643 mL | 5.9286 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1482 mL | 0.7411 mL | 1.4821 mL | 2.9643 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































