PAβN dihydrochloride (MC207110; Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide)
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $400 | In Stock |
| 500mg | $650 | In Stock |
| 1g | $975 | In Stock |
Cat #: V34158 CAS #: 100929-99-5 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: PAβN dihydrochloride (MC-207110; Phe-Arg-β-naphthylamide) is a novel and potent efflux pump inhibitor, acting on the MDR (multidrug resistance) efflux pump/transporters of some Gram-negative bacteria.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 519.47 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H32Cl2N6O2 |
| CAS No. | 100929-99-5 |
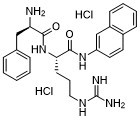
| SMILES Code | O=C([C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)NC([C@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1)=O)NC(C=C2)=CC3=C2C=CC=C3.Cl.Cl |
| Synonyms | PAssN 2HCl; PAssN-2HCl; MC-207110 2HCl; PAßN dihydrochloride; MC207110 2HCl; MC 207110 2HCl; PAßN-dihydrochloride; Phe-Arg β-naphthylamide; |
| Protocol | In Vitro | PAβN increases the susceptibilities of the three pump-overexpressing mutants of P. aeruginosa to levofloxacin 64-fold. PAβN also potentiates the activity of levofloxacin against strain PAM2391 containing plasmid pAGH97 with the mexXY genes and against wild-type strain PAM1020. PAβN has an effect on susceptibilities to other antibiotics that are substrates of efflux pumps. PAβN increases levels of accumulation of efflux pump substrates inside the cell. It enhances the activity of levofloxacin against clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa. |
|---|
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.9250 mL | 9.6252 mL | 19.2504 mL | 38.5008 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3850 mL | 1.9250 mL | 3.8501 mL | 7.7002 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1925 mL | 0.9625 mL | 1.9250 mL | 3.8501 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0963 mL | 0.4813 mL | 0.9625 mL | 1.9250 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































